Therapeutic efficacy of rifaximin loaded tamarind gum polysaccharide nanoparticles in TNBS induced IBD model Wistar rats
- PMID: 34760306
- PMCID: PMC8575354
- DOI: 10.5603/RPOR.a2021.0100
Therapeutic efficacy of rifaximin loaded tamarind gum polysaccharide nanoparticles in TNBS induced IBD model Wistar rats
Abstract
Background: Rifaximin is a non-systemic antibiotic used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Antibiotics are demonstrating a significant role in the treatment of IBD by altering the dysbiotic colonic microbiota and decreases the immunogenic and inflammatory response in the patient population. Mucoadhesive colon targeted nanoparticles provide the site-specific delivery and extended stay in the colon. Since the bacteria occupy the lumen, spread over the surface of epithelial cells, and adhere to the mucosa, delivering the rifaximin as a nanoparticles with the mucoadhesive polymer enhances the therapeutic efficacy in IBD. The objective was to fabricate and characterize the rifaximin loaded tamarind gum nanoparticles and study the therapeutic efficacy in the TNBS-induced IBD model rats.
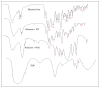
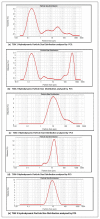
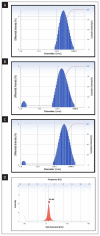
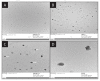
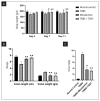
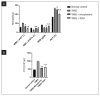
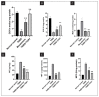
Materials and methods: The experimentation includes fabrication and characterization of drug excipient compatibility by FTIR. The fabricated nanoparticles were characterized for the hydrodynamic size and zeta potential by photon correlation spectroscopy and also analyzed by TEM. Selected best formulation was subjected to the therapeutic efficacy study in TNBS-induced IBD rats, and the macroscopic, microscopic and biochemical parameters were reported.
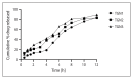
Results: The study demonstrated that the formulation TGN1 is best formulation in terms of nanoparticle characterization and hydrodynamic size which showed the hydrodynamic size of 171.4 nm and the zeta potential of -26.44 mV and other parameters such as TEM and drug release studies were also reported.
Conclusions: The therapeutic efficacy study revealed that TGN1 is efficiently reduced the IBD inflammatory conditions as compared to the TNBS control group and reference drug mesalamine group.
Keywords: IBD; nanoparticles; rifaximin; tamarind gum.
© 2021 Greater Poland Cancer Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rifaximin - Chitosan Nanoparticles for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2017;11(1):41-52. doi: 10.2174/1872213X10666161230111226. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28034350
-
Comparative Efficacy of Chitosan, Pectin Based Mesalamine Colon Targeted Drug Delivery Systems on TNBS-induced IBD Model Rats.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020;19(2):113-127. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666190118112230. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30657050
-
Colon Targeted Rifaximin Nanosuspension for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2016;15(2):101-117. doi: 10.2174/1871523015666160720103732. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27449742
-
The intriguing role of Rifaximin in gut barrier chronic inflammation and in the treatment of Crohn's disease.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018 Jun;27(6):543-551. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2018.1483333. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29865875 Review.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Zein decorated rifaximin nanosuspension: approach for sustained release and anti-bacterial efficacy enhancement.Ther Deliv. 2025 Jan;16(1):9-23. doi: 10.1080/20415990.2024.2418799. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Ther Deliv. 2025. PMID: 39530512
-
Interactions between Nanoparticles and Intestine.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 14;23(8):4339. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084339. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Treatment.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Jul 15;18:2921-2949. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S461977. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39055164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kumar J, Newton AJ. IBD Modern Concepts, Nano Drug Delivery and Patents: An Update. Recent Patents Nanomed. 2015;5(2):122–145. doi: 10.2174/1877912305666150616000003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
