Ultrastructural changes in the underactive bladder
- PMID: 34760629
- PMCID: PMC8532586
- DOI: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_153_20
Ultrastructural changes in the underactive bladder
Abstract
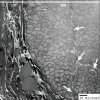
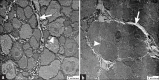
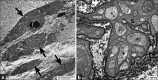
Underactive bladder (UAB) is a symptom complex suggestive of detrusor underactivity (DU). Although it implies a primary dysfunction of the detrusor muscle, many other conditions such as advanced age, neurogenic factors, and bladder outlet obstruction also lead to UAB. The current understanding of the pathophysiology directly leading to UAB is limited. We believe that by identifying the morphological changes associated with UAB might shed light on this. Therefore, we searched literature with keywords of electron microscopy, ultrastructure, UAB, and DU to review current ultrastructural evidence concerning UAB.
Keywords: Detrusor underactivity; Electron microscopy; Ultrastructure; Underactive bladder.
Copyright: © 2020 Tzu Chi Medical Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Han-Chen Ho, Dr. Yung-Hsiang Hsu, Dr. Yuan-Hong Jiang and Hann-Chorng Kuo, the editorial board members at Tzu Chi Medical Journal, had no roles in the peer review process of or decision to publish this article. The other author declared no conflicts of interest in writing this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology in lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Urology. 2003;61:37–49. - PubMed
-
- Osman NI, Esperto F, Chapple CR. Detrusor underactivity and the underactive bladder: A systematic review of preclinical and clinical studies. Eur Urol. 2018;74:633–43. - PubMed
-
- Thomas AW, Cannon A, Bartlett E, Ellis-Jones J, Abrams P. The natural history of lower urinary tract dysfunction in men: The influence of detrusor underactivity on the outcome after transurethral resection of the prostate with a minimum 10-year urodynamic follow-up. BJU Int. 2004;93:745–50. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
