Validation of the vasoactive-inotropic score in predicting pediatric septic shock mortality: A retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 34760657
- PMCID: PMC8547676
- DOI: 10.4103/IJCIIS.IJCIIS_98_20
Validation of the vasoactive-inotropic score in predicting pediatric septic shock mortality: A retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Mortality in pediatric septic shock remains very high. Vasoactive-inotropic score (VIS) is widely used to predict prognosis in patients with heart disease. It is a simple method that was initially used as a predictor of morbidity and mortality in postoperative patients with congenital heart diseases. Previous reports showed that high VIS score was associated with high mortality in pediatric sepsis. However, its discriminative value remains unclear. We aim to explore the discriminative value of VIS in predicting mortality in pediatric septic shock patients.
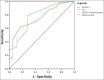
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study on medical records of septic shock patients who received care in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). We screened medical records of pediatric patients which were diagnosed with septic shock and admitted to the PICU and received vasoactive/inotropic score for more than 8 h. Other supporting examination results were recorded, such as organ function evaluation for calculation of Pediatric Logistic Organ Dysfunction-2 (PELOD-2) score. The outcome of patients was recorded. The receiver operating curve was constructed to calculate the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity of each cutoff point.
Results: We obtained the optimum cutoff point of VIS > 11 with 78.87% sensitivity and 72.22% specificity. AUC positive was 0.779 (P < 0.001); predictive value and negative predictive value were 91.80% and 46.43%, respectively.
Conclusion: VIS > 11 has a good ability to predict mortality in children with septic shock.
Keywords: Mortality; pediatrics; sepsis; vasoactive-inotropic score.
Copyright: © 2021 International Journal of Critical Illness and Injury Science.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A. International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis. International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: Definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005;6:2–4. - PubMed
-
- Leteurtre S, Duhamel A, Salleron J, Grandbastien B, Lacroix J, Leclerc F, et al. PELOD-2: An update of the PEdiatric logistic organ dysfunction score. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:1761–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources