MicroRNAs Role in Breast Cancer: Theranostic Application in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 34760689
- PMCID: PMC8573223
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.717759
MicroRNAs Role in Breast Cancer: Theranostic Application in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
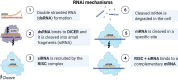
Breast cancer is an aggressive silent disease, representing 11.7% of the diagnosed cancer worldwide, and it is also a leading cause of death in Saudi Arabia. Consequently, microRNAs have emerged recently as potential biomarkers to diagnose and monitor such cases at the molecular level, which tends to be problematic during diagnosis. MicroRNAs are highly conserved non- coding oligonucleotide RNA. Over the last two decades, studies have determined the functional significance of these small RNAs and their impact on cellular development and the interaction between microRNAs and messenger RNAs, which affect numerous molecular pathways and physiological functions. Moreover, many disorders, including breast cancer, are associated with the dysregulation of microRNA. Sparingly, many microRNAs can suppress cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and vice versa. Remarkably, microRNAs can be harvested from patients' biofluids to predict disease progression that considered a non-invasive method. Nevertheless, MicroRNAs are currently utilized as anti- cancer therapies combined with other drug therapies or even as a single agents' treatment. Therefore, this review will focus on microRNAs' role in breast cancer as an indicator of disease progression. In addition, this review summarizes the current knowledge of drug sensitivity and methods in detecting microRNA and their application to improve patient care and identifies the current gaps in this field.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; anticancer therapy; breast cancer metastasis; chemotherapy resistance; circulating biomarkers; miRNA; molecular pathways.
Copyright © 2021 Alyami.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

