Tumor Suppressor FBXW7 and Its Regulation of DNA Damage Response and Repair
- PMID: 34760892
- PMCID: PMC8573206
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.751574
Tumor Suppressor FBXW7 and Its Regulation of DNA Damage Response and Repair
Abstract
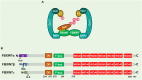
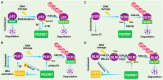
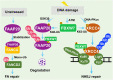
The proper DNA damage response (DDR) and repair are the central molecular mechanisms for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and genomic integrity. The abnormality in this process is frequently observed in human cancers, and is an important contributing factor to cancer development. FBXW7 is an F-box protein serving as the substrate recognition component of SCF (SKP1-CUL1-F-box protein) E3 ubiquitin ligase. By selectively targeting many oncoproteins for proteasome-mediated degradation, FBXW7 acts as a typical tumor suppressor. Recent studies have demonstrated that FBXW7 also plays critical roles in the process of DDR and repair. In this review, we first briefly introduce the processes of protein ubiquitylation by SCFFBXW7 and DDR/repair, then provide an overview of the molecular characteristics of FBXW7. We next discuss how FBXW7 regulates the process of DDR and repair, and its translational implication. Finally, we propose few future perspectives to further elucidate the role of FBXW7 in regulation of a variety of biological processes and tumorigenesis, and to design a number of approaches for FBXW7 reactivation in a subset of human cancers for potential anticancer therapy.
Keywords: DDR; DNA repair; FBXW7; cancer; ubiquitylation.
Copyright © 2021 Lan and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bahram F., von der Lehr N., Cetinkaya C., Larsson L. G. (2000). c-Myc hot spot mutations in lymphomas result in inefficient ubiquitination and decreased proteasome-mediated turnover. Blood 95 2104–2110. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

