miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
- PMID: 34761115
- PMCID: PMC8569285
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2021-0357
miR-150-5p affects AS plaque with ASMC proliferation and migration by STAT1
Abstract
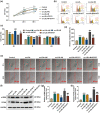
We explore miR-150-5p in atherosclerosis (AS). The AS model was constructed using Apo E-/- mice with an injection of the miR-150-5p mimic or an inhibitor. Pathological characteristics were assessed using Oil red O staining and Masson staining. Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot were used to analyze the expressions of microRNA-150-5p (miR-150-5p), STAT1, α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). Targetscan and dual-luciferase reporter assay were used to analyze the interaction between miR-150-5p and STAT1. The viability, migration, cell cycle and α-SMA and PCNA expressions in oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-stimulated primary human aortic smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) were assessed using molecular experiments. miR-150-5p was reduced in both AS mice and ox-LDL-stimulated human aortic smooth muscle cells but STAT1 had the opposite effect. The miR-150-5p inhibitor alleviated the increase of lipid plaque and reduced collagen accumulation in the aortas during AS. Upregulation of α-SMA and PCNA was reversed by miR-150-5p upregulation. STAT1 was targeted by miR-150-5p, and overexpressed miR-150-5p weakened the ox-LDL-induced increase of viability and migration abilities and blocked cell cycle in ASMCs, but overexpressed STAT1 blocked the effect of the miR-150-5p mimic. This paper demonstrates that miR-150-5p has potential as a therapeutic target in AS, with plaque stabilization by regulating ASMC proliferation and migration via STAT1.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; collagen metabolism; miR-150-5p; plaque stability; signal transducer and activator of transcription 1.
© 2021 Yuan Bian et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lüscher TF, Landmesser U, von Eckardstein A, Fogelman AM. High-density lipoprotein: vascular protective effects, dysfunction, and potential as therapeutic target. Circ Res. 2014;114(1):171–82. - PubMed
- Lüscher TF, Landmesser U, von Eckardstein A, Fogelman AM. High-density lipoprotein: vascular protective effects, dysfunction, and potential as therapeutic target. Circ Res. 2014;114(1):171–82. - PubMed
-
- Billon C, Sitaula S, Burris TP. Inhibition of RORα/γ suppresses atherosclerosis via inhibition of both cholesterol absorption and inflammation. Mol Metab. 2016;5(10):997–1005. - PMC - PubMed
- Billon C, Sitaula S, Burris TP. Inhibition of RORα/γ suppresses atherosclerosis via inhibition of both cholesterol absorption and inflammation. Mol Metab. 2016;5(10):997–1005. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
