"Venice marathon": participation of female Master Athletes shows a constant increase from 2003 to 2019
- PMID: 34761670
- PMCID: PMC8758960
- DOI: 10.4081/ejtm.2021.10266
"Venice marathon": participation of female Master Athletes shows a constant increase from 2003 to 2019
Abstract
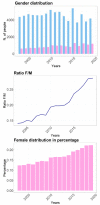
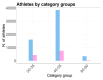
The marathon is the most classic Olympic running event. In several cities worldwide it has become very popular with participation increasing during the last 20 years, particularly by Master Athletes. There are evidences that long-distance running could provide considerable health benefits for older runners, specifically risk reduction of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, depression, and falls. Several studies have focused on the distribution of participants and their performance on famous marathons such as those of Berlin, Boston and New York. In this preliminary study we have analyzed data from several editions of the Venice marathon, a famous Italian race that attracts people from every corner of the world. The Venice marathon is listed in Abbott World Marathon Majors Wanda Age Group World Ranking and is Bronze Label certificated by IAAF, and Gold Label by FIDAL. The marathon starts outside Venice near Stra, then runs along the Brenta Riviera to Venice where the runners cross the canals over floating bridges set up for the race. For this study we analyzed data of the Venice marathon describing gender distribution in 17 editions (2003-2019), but groups of age-categories and their nationality only in 13 editions from 2007 to 2019. The analysis shows a steady increase in female participation, from 2003 to 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirms that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures


References
-
- Roelands B, de Koning J, Foster C, Hettinga F, Meeusen R. Neurophysiological determinants of theoretical concepts and mechanisms involved in pacing. Sports Med. 2013. May;43(5):301-11. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0030-4. - PubMed
-
- Coyle EF. Physiological regulation of marathon performance. Sports Med. 2007;37(4-5):306-11. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200737040-00009. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

