A randomized controlled clinical trial on efficacy and safety of anakinra in patients with severe COVID-19
- PMID: 34762351
- PMCID: PMC8652881
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.563
A randomized controlled clinical trial on efficacy and safety of anakinra in patients with severe COVID-19
Abstract
Introduction: Hyperinflammatory state has a role in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Anakinra could reduce inflammation and help to combat the condition. In this study, we aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of anakinra (PerkinRA®) in severe COVID-19.
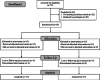
Method: The study was an open-label, randomized, controlled trial conducted in Imam Hossein Medical Center from May to July 2020. Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 were included in this study. We administered anakinra 100 mg daily intravenously. All patients received COVID-19 pharmacotherapy based on the represented national guideline. The need for invasive mechanical ventilation is considered the primary outcome.
Results: Thirty patients were included in this study, and 15 of them received Anakinra. Nineteen patients were male (63.3%), and 11 were female (36.7%). The mean age of patients was 55.77 ± 15.89 years. In the intervention group, the need for invasive mechanical ventilation was significantly reduced compared to the control group (20.0% vs. 66.7%, p = .010). Also, these patients had a significantly lower length of hospital stay (p = .043). No significant higher rate of infection was recorded.
Conclusion: Anakinra as an immunomodulatory agent has been associated with the reduced need for mechanical ventilation in patients admitted to intensive care units because of severe COVID-19. The medication reduced the hospital length of stay. Furthermore, no increased risk of infection was observed. Further randomized placebo-controlled trials with a larger sample size are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute respiratory distress syndrome; anakinra; coronavirus; inflammation; interleukin-1 inhibitor; mortality.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO coronavirus disease (COVID‐19) dashboard. 2021. Accessed October 8, 2021. https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Ziaie S, Koucheck M, Miri M, et al. Review of therapeutic agents for the treatment of COVID‐19. J Cell Mol Anesth. 2020;5(1):32‐36. 10.22037/jcma.v5i1.29760 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical