Long-term efficacy and safety of eladocagene exuparvovec in patients with AADC deficiency
- PMID: 34763085
- PMCID: PMC8822132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.005
Long-term efficacy and safety of eladocagene exuparvovec in patients with AADC deficiency
Abstract
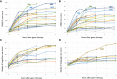
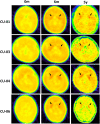
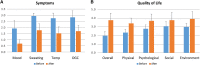
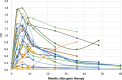
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency results in decreased neurotransmitter levels and severe motor dysfunction. Twenty-six patients without head control received bilateral intraputaminal infusions of a recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2 vector containing the human aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase gene (eladocagene exuparvovec) and have completed 1-year evaluations. Rapid improvements in motor and cognitive function occurred within 12 months after gene therapy and were sustained during follow-up for >5 years. An increase in dopamine production was demonstrated by positron emission tomography and neurotransmitter analysis. Patient symptoms (mood, sweating, temperature, and oculogyric crises), patient growth, and patient caretaker quality of life improved. Although improvements were observed in all treated participants, younger age was associated with greater improvement. There were no treatment-associated brain injuries, and most adverse events were related to underlying disease. Post-surgery complications such as cerebrospinal fluid leakage were managed with standard of care. Most patients experienced mild to moderate dyskinesia that resolved in a few months. These observations suggest that eladocagene exuparvovec treatment for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency provides durable and meaningful benefits with a favorable safety profile.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01395641 NCT02926066.
Keywords: adeno-associated virus; aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency; eladocagene exuparvovec; gene therapy; putamen.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.-H.T. and S.-H.T. have nothing to disclose. B.J.B. has served as an advisory board member for Pfizer, RDRU, AavantBio, and SAB. He has received consulting fees from Pfizer and AavantBio. He is a stock owner of AavantBio, an employee of the University of Florida, and a research investigator for NIH Awards. Y.-H.C. participated as an advisory board member of Asklepios BioPharmaceutical, Amicus, Biogen, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. He has received consulting fees from Abeona, Biogen, Novartis, and PTC Therapeutics. He has also served as a research investigator for Biogen and Sanofi and as a speaker for Avexis, Biogen, BioMarin, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. W.-L.H. participated as an advisory board member, received consulting fees, and was a speaker for PTC Therapeutics, BioMarin, and Sanofi. He was a grant recipient for PTC Therapeutics and BioMarin and a research investigator for PTC Therapeutics. N.-C.L. has received consulting fees from PTC Therapeutics. S.-I.M. is an employee, has served as a research investigator, and owns stock in Gene Therapy Research Institution, which commercializes the use of AAV2 vectors for gene therapy applications. He participated as an advisory board member and received consulting fees for PTC Therapeutics. To the extent that the work in this manuscript increases the value of these commercial holdings, they have a conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Himmelreich N., Montioli R., Bertoldi M., Carducci C., Leuzzi V., Gemperle C., Berner T., Hyland K., Thöny B., Hoffmann G.F., et al. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: molecular and metabolic basis and therapeutic outlook. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019;127:12–22. - PubMed
-
- Hyland K., Clayton P.T. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency in twins. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1990;13:301–304. - PubMed
-
- Brun L., Ngu L.H., Keng W.T., Ch'Ng G.S., Choy Y.S., Hwu W.L., Lee W.T., Willemsen M.A.A.P., Verbeek M.M., Wassenberg T., et al. Clinical and biochemical features of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Neurology. 2010;75:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Pons R., Ford B., Chiriboga C.A., Clayton P.T., Hinton V., Hyland K., Sharma R., De Vivo D.C. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: clinical features, treatment, and prognosis. Neurology. 2004;62:1058–1065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

