In-vitro cytokine production and nasopharyngeal microbiota composition in the early stage of COVID-19 infection
- PMID: 34763156
- PMCID: PMC8570934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155757
In-vitro cytokine production and nasopharyngeal microbiota composition in the early stage of COVID-19 infection
Abstract
Background: To determine and compare nasopharyngeal microbiota (NM) composition, in vitro basal (Nil tube), provoked (Mitogen tube) production of cytokines at the early stage of COVID-19.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 4 age and sex-matched study groups; group 1 (recovered COVID-19) (n = 26), group 2 (mild COVID-19) (n = 24), group 3 (severe COVID-19) (n = 25), and group 4 (healthy controls) (n = 25). The study parameters obtained from the COVID-19 (group 2, and 3) at the early phase of hospital admission.
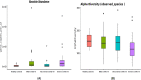
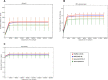
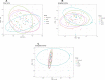
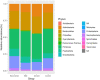
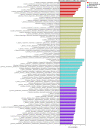
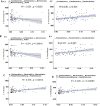
Results: The results from the reaserch deoicted that the Mean ± SD age was 53.09 ± 14.51 years. Some of the in vitro cytokines production was significantly different between the study groups. Some of the findinggs on cytokines depicted a significant differences between study groups were interleukin (IL)-1β Nil, IL-1β Mitogen, and their subtraction (i.e Mitogen-Nil). Regarding IL-10, and IL-17a levels, Mitogen, and Mitogen-Nil tube production levels were significantly different between the groups. Surprisingly, most of these measures were lowest in the severe COVID-19 patients' group. Using discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe), Taxa of NM with significant abundance was determined. About 20 taxa with an LDA score > 4 were identified as candidate biomarkers. Some of these taxa showed a significant correlation with IL-1β and IL-10 Mitogen and Mitogen- Nil levels (R > 0.3 or < -0.3, p < 0.05).
Conclusions: The findings of this perticular study regarting the early stage of COVID-19 showed that in vitro cytokines production, studies might be more useful than the ordinary cytokines' blood level measurement. Besides, the study identified some NM species that could be candidate biomarkers in managing this infection. However, further detailed studies are needed in these fields.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cytokine; Dysbiosis; In-vitro; Microbiota; Quantiferon test; Virus.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Han H., Ma Q., Li C., Liu R., Zhao L., Wang W., Zhang P., Liu X., Gao G., Liu F., Jiang Y., Cheng X., Zhu C., Xia Y. Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020;9:1123–1130. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

