Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network
- PMID: 34764548
- PMCID: PMC7474514
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-01829-7
Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network
Abstract
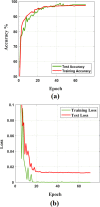
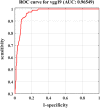
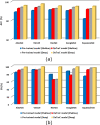
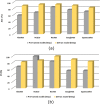
Chest X-ray is the first imaging technique that plays an important role in the diagnosis of COVID-19 disease. Due to the high availability of large-scale annotated image datasets, great success has been achieved using convolutional neural networks (CNN s) for image recognition and classification. However, due to the limited availability of annotated medical images, the classification of medical images remains the biggest challenge in medical diagnosis. Thanks to transfer learning, an effective mechanism that can provide a promising solution by transferring knowledge from generic object recognition tasks to domain-specific tasks. In this paper, we validate and a deep CNN, called Decompose, Transfer, and Compose (DeTraC), for the classification of COVID-19 chest X-ray images. DeTraC can deal with any irregularities in the image dataset by investigating its class boundaries using a class decomposition mechanism. The experimental results showed the capability of DeTraC in the detection of COVID-19 cases from a comprehensive image dataset collected from several hospitals around the world. High accuracy of 93.1% (with a sensitivity of 100%) was achieved by DeTraC in the detection of COVID-19 X-ray images from normal, and severe acute respiratory syndrome cases.
Keywords: COVID-19 detection; Chest X-ray images; Covolutional neural networks; Data irregularities; DeTraC.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Figures


References
-
- Abbas A, Abdelsamea MM (2018) Learning transformations for automated classification of manifestation of tuberculosis using convolutional neural network. In: 2018 13Th international conference on computer engineering and systems (ICCES), IEEE, pp 122–126
-
- Abbas A, Abdelsamea MM, Gaber MM. Detrac: Transfer learning of class decomposed medical images in convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access. 2020;8:74901–74913. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989273. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
