OptCoNet: an optimized convolutional neural network for an automatic diagnosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 34764551
- PMCID: PMC7502308
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-01904-z
OptCoNet: an optimized convolutional neural network for an automatic diagnosis of COVID-19
Abstract
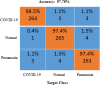
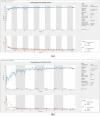
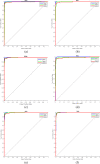
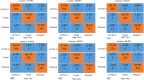
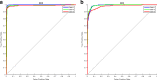
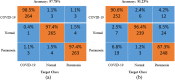
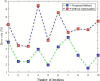
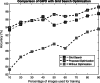
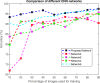
The quick spread of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has become a global concern and affected more than 15 million confirmed patients as of July 2020. To combat this spread, clinical imaging, for example, X-ray images, can be utilized for diagnosis. Automatic identification software tools are essential to facilitate the screening of COVID-19 using X-ray images. This paper aims to classify COVID-19, normal, and pneumonia patients from chest X-ray images. As such, an Optimized Convolutional Neural network (OptCoNet) is proposed in this work for the automatic diagnosis of COVID-19. The proposed OptCoNet architecture is composed of optimized feature extraction and classification components. The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) algorithm is used to optimize the hyperparameters for training the CNN layers. The proposed model is tested and compared with different classification strategies utilizing an openly accessible dataset of COVID-19, normal, and pneumonia images. The presented optimized CNN model provides accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1 score values of 97.78%, 97.75%, 96.25%, 92.88%, and 95.25%, respectively, which are better than those of state-of-the-art models. This proposed CNN model can help in the automatic screening of COVID-19 patients and decrease the burden on medicinal services frameworks.
Keywords: Automatic diagnosis; COVID-19; Convolutional neural network; Coronavirus; Grey wolf optimizer; Stochastic gradient descent.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
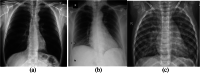

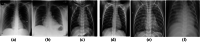
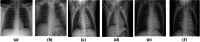
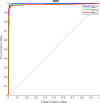
References
-
- Calvo C, López-Hortelano MG, De Carlos Vicente JC, Martínez JLV, De Trabajo de la Asociación G (2020) Recommendations on the clinical management of the COVID-19 infection by the «new coronavirus» SARS-CoV2. Spanish Paediatric Association working group. An Pediatría (English Edition) 92(4):241.e1–241.e11 - PMC - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic (20120, February). Worldometers, Retrieved July 23, 2020, from https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?utm_campaign=homeAdvegas1?
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
