Deep learning based detection and analysis of COVID-19 on chest X-ray images
- PMID: 34764553
- PMCID: PMC7544769
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-01902-1
Deep learning based detection and analysis of COVID-19 on chest X-ray images
Abstract
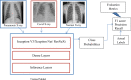
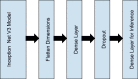
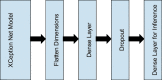
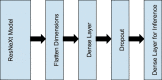
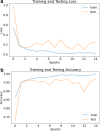
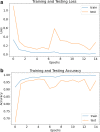
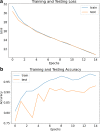
Covid-19 is a rapidly spreading viral disease that infects not only humans, but animals are also infected because of this disease. The daily life of human beings, their health, and the economy of a country are affected due to this deadly viral disease. Covid-19 is a common spreading disease, and till now, not a single country can prepare a vaccine for COVID-19. A clinical study of COVID-19 infected patients has shown that these types of patients are mostly infected from a lung infection after coming in contact with this disease. Chest x-ray (i.e., radiography) and chest CT are a more effective imaging technique for diagnosing lunge related problems. Still, a substantial chest x-ray is a lower cost process in comparison to chest CT. Deep learning is the most successful technique of machine learning, which provides useful analysis to study a large amount of chest x-ray images that can critically impact on screening of Covid-19. In this work, we have taken the PA view of chest x-ray scans for covid-19 affected patients as well as healthy patients. After cleaning up the images and applying data augmentation, we have used deep learning-based CNN models and compared their performance. We have compared Inception V3, Xception, and ResNeXt models and examined their accuracy. To analyze the model performance, 6432 chest x-ray scans samples have been collected from the Kaggle repository, out of which 5467 were used for training and 965 for validation. In result analysis, the Xception model gives the highest accuracy (i.e., 97.97%) for detecting Chest X-rays images as compared to other models. This work only focuses on possible methods of classifying covid-19 infected patients and does not claim any medical accuracy.
Keywords: CNN; Chest X-ray images; Covid-19; Deep-learning; Inception net 3; ResNeXt; XCeption.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of COVID-19 from Multimodal Imaging Data Using Optimized Deep Learning Techniques.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(3):212. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01653-5. Epub 2023 Feb 17. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36811125 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized Xception Learning Model and XgBoost Classifier for Detection of Multiclass Chest Disease from X-ray Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 3;13(15):2583. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152583. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568946 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 prediction based on hybrid Inception V3 with VGG16 using chest X-ray images.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 Jun 5:1-18. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15903-y. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 37362699 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review: Chest radiography images (X-ray images) analysis and COVID-19 categorization diagnosis using artificial intelligence techniques.Network. 2023 Feb-Feb;34(1-2):26-64. doi: 10.1080/0954898X.2022.2147231. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Network. 2023. PMID: 36420865
-
Application of Machine Learning in Diagnosis of COVID-19 Through X-Ray and CT Images: A Scoping Review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 25;8:638011. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.638011. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33842563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anomaly Detection in COVID-19 Time-Series Data.SN Comput Sci. 2021;2(4):279. doi: 10.1007/s42979-021-00658-w. Epub 2021 May 19. SN Comput Sci. 2021. PMID: 34027432 Free PMC article.
-
Handling class imbalance in COVID-19 chest X-ray images classification: Using SMOTE and weighted loss.Appl Soft Comput. 2022 Nov;129:109588. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109588. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Appl Soft Comput. 2022. PMID: 36061418 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging to combat coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a detailed review with direction for future research.Artif Intell Rev. 2022;55(2):1409-1439. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-09985-z. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Artif Intell Rev. 2022. PMID: 33875900 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for COVID-19 Screening Using Radiological Imaging: A Comprehensive Review.SN Comput Sci. 2023;4(1):65. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01464-8. Epub 2022 Nov 24. SN Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 36467853 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning-based approach for diagnosing COVID-19 on chest x-ray images, and a test study with clinical experts.Comput Intell. 2022 May 17:10.1111/coin.12526. doi: 10.1111/coin.12526. Online ahead of print. Comput Intell. 2022. PMID: 35941907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xie X, Li X, Wan S, Gong Y. Data Mining. Berlin: Springer; 2006. Mining x-ray images of SARS patients; pp. 282–294.
-
- Wang Y, Hu M, Li Q, Zhang XP, Zhai G, Yao N (2020) Abnormal respiratory patterns classifier may contribute to large-scale screening of people infected with COVID-19 in an accurate and unobtrusive manner. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.05534
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
