Automated diagnosis of COVID-19 with limited posteroanterior chest X-ray images using fine-tuned deep neural networks
- PMID: 34764554
- PMCID: PMC7568031
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-01900-3
Automated diagnosis of COVID-19 with limited posteroanterior chest X-ray images using fine-tuned deep neural networks
Abstract
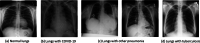
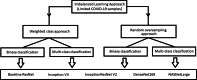
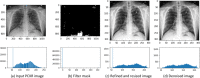
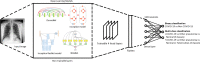
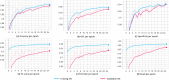
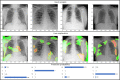
The novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory syndrome that resembles pneumonia. The current diagnostic procedure of COVID-19 follows reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) based approach which however is less sensitive to identify the virus at the initial stage. Hence, a more robust and alternate diagnosis technique is desirable. Recently, with the release of publicly available datasets of corona positive patients comprising of computed tomography (CT) and chest X-ray (CXR) imaging; scientists, researchers and healthcare experts are contributing for faster and automated diagnosis of COVID-19 by identifying pulmonary infections using deep learning approaches to achieve better cure and treatment. These datasets have limited samples concerned with the positive COVID-19 cases, which raise the challenge for unbiased learning. Following from this context, this article presents the random oversampling and weighted class loss function approach for unbiased fine-tuned learning (transfer learning) in various state-of-the-art deep learning approaches such as baseline ResNet, Inception-v3, Inception ResNet-v2, DenseNet169, and NASNetLarge to perform binary classification (as normal and COVID-19 cases) and also multi-class classification (as COVID-19, pneumonia, and normal case) of posteroanterior CXR images. Accuracy, precision, recall, loss, and area under the curve (AUC) are utilized to evaluate the performance of the models. Considering the experimental results, the performance of each model is scenario dependent; however, NASNetLarge displayed better scores in contrast to other architectures, which is further compared with other recently proposed approaches. This article also added the visual explanation to illustrate the basis of model classification and perception of COVID-19 in CXR images.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-ray (CXR); Classification; Deep learning; Imbalanced learning; Pneumonia; Transfer learning.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Explainable COVID-19 Detection Based on Chest X-rays Using an End-to-End RegNet Architecture.Viruses. 2023 Jun 6;15(6):1327. doi: 10.3390/v15061327. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376626 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of coronavirus disease from X-ray images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(5):841-850. doi: 10.3233/XST-200720. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32804113 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Transfer Learning-based ResNet models in Chest X-ray image classification for detecting COVID-19 Pneumonia.Chemometr Intell Lab Syst. 2022 May 15;224:104534. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2022.104534. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst. 2022. PMID: 35291673 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 diagnosis: A comprehensive review of pre-trained deep learning models based on feature extraction algorithm.Results Eng. 2023 Jun;18:101020. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101020. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Results Eng. 2023. PMID: 36945336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Handling class imbalance in COVID-19 chest X-ray images classification: Using SMOTE and weighted loss.Appl Soft Comput. 2022 Nov;129:109588. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109588. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Appl Soft Comput. 2022. PMID: 36061418 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review of Learning Models.Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2022;29(3):1915-1940. doi: 10.1007/s11831-021-09641-3. Epub 2021 Sep 18. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2022. PMID: 34566404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning-based prediction of COVID-19 diagnosis based on symptoms.NPJ Digit Med. 2021 Jan 4;4(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00372-6. NPJ Digit Med. 2021. PMID: 33398013 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing a real-time, AI-based, people detection and social distancing measuring system for Covid-19.J Real Time Image Process. 2021;18(6):1937-1947. doi: 10.1007/s11554-021-01070-6. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Real Time Image Process. 2021. PMID: 33500738 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of deep learning approaches for identification of different corona-virus species and time series prediction.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2021 Jun;90:101921. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101921. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2021. PMID: 33930734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afshar P, Heidarian S, Naderkhani F, Oikonomou A, Plataniotis KN, Mohammadi A (2020) Covid-caps: a capsule network-based framework for identification of covid-19 cases from x-ray images. arXiv:2004.02696 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bukhari SUK, Bukhari SSK, Syed A, SHAH SSH (2020) The diagnostic evaluation of convolutional neural network (cnn) for the assessment of chest x-ray of patients infected with covid-19. medRxiv
-
- Chen Q, Montesinos P, Sun QS, Heng PA, et al. Adaptive total variation denoising based on difference curvature. Image Vis Comput. 2010;28(3):298–306. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2009.04.012. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
