A new deep learning pipeline to detect Covid-19 on chest X-ray images using local binary pattern, dual tree complex wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 34764560
- PMCID: PMC7609830
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-02019-1
A new deep learning pipeline to detect Covid-19 on chest X-ray images using local binary pattern, dual tree complex wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks
Abstract
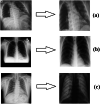
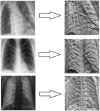
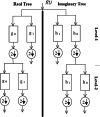
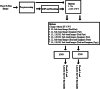
In this study, which aims at early diagnosis of Covid-19 disease using X-ray images, the deep-learning approach, a state-of-the-art artificial intelligence method, was used, and automatic classification of images was performed using convolutional neural networks (CNN). In the first training-test data set used in the study, there were 230 X-ray images, of which 150 were Covid-19 and 80 were non-Covid-19, while in the second training-test data set there were 476 X-ray images, of which 150 were Covid-19 and 326 were non-Covid-19. Thus, classification results have been provided for two data sets, containing predominantly Covid-19 images and predominantly non-Covid-19 images, respectively. In the study, a 23-layer CNN architecture and a 54-layer CNN architecture were developed. Within the scope of the study, the results were obtained using chest X-ray images directly in the training-test procedures and the sub-band images obtained by applying dual tree complex wavelet transform (DT-CWT) to the above-mentioned images. The same experiments were repeated using images obtained by applying local binary pattern (LBP) to the chest X-ray images. Within the scope of the study, four new result generation pipeline algorithms having been put forward additionally, it was ensured that the experimental results were combined and the success of the study was improved. In the experiments carried out in this study, the training sessions were carried out using the k-fold cross validation method. Here the k value was chosen as 23 for the first and second training-test data sets. Considering the average highest results of the experiments performed within the scope of the study, the values of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, F-1 score, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for the first training-test data set were 0,9947, 0,9800, 0,9843, 0,9881 and 0,9990 respectively; while for the second training-test data set, they were 0,9920, 0,9939, 0,9891, 0,9828 and 0,9991; respectively. Within the scope of the study, finally, all the images were combined and the training and testing processes were repeated for a total of 556 X-ray images comprising 150 Covid-19 images and 406 non-Covid-19 images, by applying 2-fold cross. In this context, the average highest values of sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, F-1 score, and AUC for this last training-test data set were found to be 0,9760, 1,0000, 0,9906, 0,9823 and 0,9997; respectively.
Keywords: Chest X-ray classification; Convolutional neural networks (CNN); Corona 2019; Covid-19; Deep learning; Dual tree complex wavelet transform (DT-CWT); Local binary pattern (LBP).
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestDr. Ceylan declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mr. Yasar declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel study for automatic two-class COVID-19 diagnosis (between COVID-19 and Healthy, Pneumonia) on X-ray images using texture analysis and 2-D/3-D convolutional neural networks.Multimed Syst. 2022 Jan 29:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00892-z. Online ahead of print. Multimed Syst. 2022. PMID: 35125671 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Approaches to Improve Classification Parameters for Diagnosing COVID-19 from CT Images.Cognit Comput. 2021 Jul 15:1-28. doi: 10.1007/s12559-021-09915-9. Online ahead of print. Cognit Comput. 2021. PMID: 34306240 Free PMC article.
-
A novel comparative study for detection of Covid-19 on CT lung images using texture analysis, machine learning, and deep learning methods.Multimed Tools Appl. 2021;80(4):5423-5447. doi: 10.1007/s11042-020-09894-3. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Multimed Tools Appl. 2021. PMID: 33041635 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey on Deep Learning in COVID-19 Diagnosis.J Imaging. 2022 Dec 20;9(1):1. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9010001. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36662099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-CAPS: A capsule network-based framework for identification of COVID-19 cases from X-ray images.Pattern Recognit Lett. 2020 Oct;138:638-643. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.09.010. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Pattern Recognit Lett. 2020. PMID: 32958971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel study for automatic two-class COVID-19 diagnosis (between COVID-19 and Healthy, Pneumonia) on X-ray images using texture analysis and 2-D/3-D convolutional neural networks.Multimed Syst. 2022 Jan 29:1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00530-022-00892-z. Online ahead of print. Multimed Syst. 2022. PMID: 35125671 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning-Based Research for COVID-19 Detection, Diagnosis, and Prediction: A Survey.SN Comput Sci. 2022;3(4):286. doi: 10.1007/s42979-022-01184-z. Epub 2022 May 12. SN Comput Sci. 2022. PMID: 35578678 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 prediction based on hybrid Inception V3 with VGG16 using chest X-ray images.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 Jun 5:1-18. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-15903-y. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 37362699 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 deep classification network based on convolution and deconvolution local enhancement.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Aug;135:104588. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104588. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34182330 Free PMC article.
-
Robotics and artificial intelligence in healthcare during COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.Rob Auton Syst. 2021 Dec;146:103902. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2021.103902. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Rob Auton Syst. 2021. PMID: 34629751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albarello F, Pianura E, Stefanoa FD, Cristofaro M, Petrone A, Marchioni L, Palazzolo C, Schininà V, Nicastri E, Petrosillo N, Campioni P, Eskild P, Zumla A, Ippolito G. 2019-novel coronavirus severe adult respiratory distress syndrome in two cases in Italy: an uncommon radiological presentation. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;93:192–197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.02.043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
