Design and analysis of a large-scale COVID-19 tweets dataset
- PMID: 34764561
- PMCID: PMC7646503
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-02029-z
Design and analysis of a large-scale COVID-19 tweets dataset
Abstract
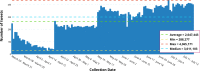
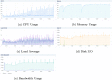
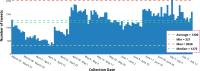
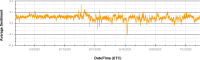
As of July 17, 2020, more than thirteen million people have been diagnosed with the Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19), and half a million people have already lost their lives due to this infectious disease. The World Health Organization declared the COVID-19 outbreak as a pandemic on March 11, 2020. Since then, social media platforms have experienced an exponential rise in the content related to the pandemic. In the past, Twitter data have been observed to be indispensable in the extraction of situational awareness information relating to any crisis. This paper presents COV19Tweets Dataset (Lamsal 2020a), a large-scale Twitter dataset with more than 310 million COVID-19 specific English language tweets and their sentiment scores. The dataset's geo version, the GeoCOV19Tweets Dataset (Lamsal 2020b), is also presented. The paper discusses the datasets' design in detail, and the tweets in both the datasets are analyzed. The datasets are released publicly, anticipating that they would contribute to a better understanding of spatial and temporal dimensions of the public discourse related to the ongoing pandemic. As per the stats, the datasets (Lamsal 2020a, 2020b) have been accessed over 74.5k times, collectively.
Keywords: Crisis computing; Network analysis; Sentiment analysis; Social computing; Twitter data.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestsThe author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MonkeyPox2022Tweets: A Large-Scale Twitter Dataset on the 2022 Monkeypox Outbreak, Findings from Analysis of Tweets, and Open Research Questions.Infect Dis Rep. 2022 Nov 14;14(6):855-883. doi: 10.3390/idr14060087. Infect Dis Rep. 2022. PMID: 36412745 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking discussions of complementary, alternative, and integrative medicine in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic: a month-by-month sentiment analysis of Twitter data.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Apr 13;22(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03586-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35418205 Free PMC article.
-
Twitter conversations predict the daily confirmed COVID-19 cases.Appl Soft Comput. 2022 Nov;129:109603. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109603. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Appl Soft Comput. 2022. PMID: 36092470 Free PMC article.
-
Topics, Trends, and Sentiments of Tweets About the COVID-19 Pandemic: Temporal Infoveillance Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Oct 23;22(10):e22624. doi: 10.2196/22624. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33006937 Free PMC article.
-
An augmented multilingual Twitter dataset for studying the COVID-19 infodemic.Soc Netw Anal Min. 2021;11(1):102. doi: 10.1007/s13278-021-00825-0. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Soc Netw Anal Min. 2021. PMID: 34697560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissecting the infodemic: An in-depth analysis of COVID-19 misinformation detection on X (formerly Twitter) utilizing machine learning and deep learning techniques.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 12;10(18):e37760. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37760. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39315207 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 sentiment analysis via deep learning during the rise of novel cases.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 19;16(8):e0255615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255615. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34411112 Free PMC article.
-
Examining media's coverage of COVID-19 vaccines and social media sentiments on vaccine manufacturers' stock prices.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 13;12:1411345. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1411345. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39193202 Free PMC article.
-
Sentiment Analysis on COVID-19-Related Social Distancing in Canada Using Twitter Data.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 3;18(11):5993. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115993. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34204907 Free PMC article.
-
Topics and Sentiments of Public Concerns Regarding COVID-19 Vaccines: Social Media Trend Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 21;23(10):e30765. doi: 10.2196/30765. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34581682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alqurashi S, Alhindi A, Alanazi E (2020) Large arabic twitter dataset on covid-19. arXiv:2004.04315
-
- Banda JM, Tekumalla R, Wang G, Yu J, Liu T, Ding Y, Chowell G (2020) A large-scale covid-19 twitter chatter dataset for open scientific research–an international collaboration. arXiv:2004.03688 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett NC, Millard DE, Martin D (2018) Assessing twitter geocoding resolution. In: Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Web Science, pp 239–243
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
