Multilingual topic modeling for tracking COVID-19 trends based on Facebook data analysis
- PMID: 34764585
- PMCID: PMC7881346
- DOI: 10.1007/s10489-020-02033-3
Multilingual topic modeling for tracking COVID-19 trends based on Facebook data analysis
Abstract
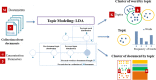
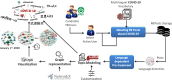
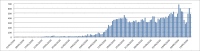
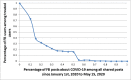
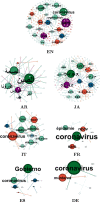
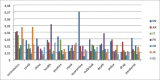
Social data has shown important role in tracking, monitoring and risk management of disasters. Indeed, several works focused on the benefits of social data analysis for the healthcare practices and curing domain. Similarly, these data are exploited now for tracking the COVID-19 pandemic but the majority of works exploited Twitter as source. In this paper, we choose to exploit Facebook, rarely used, for tracking the evolution of COVID-19 related trends. In fact, a multilingual dataset covering 7 languages (English (EN), Arabic (AR), Spanish (ES), Italian (IT), German (DE), French (FR) and Japanese (JP)) is extracted from Facebook public posts. The proposal is an analytics process including a data gathering step, pre-processing, LDA-based topic modeling and presentation module using graph structure. Data analysing covers the duration spanned from January 1st, 2020 to May 15, 2020 divided on three periods in cumulative way: first period January-February, second period March-April and the last one to 15 May. The results showed that the extracted topics correspond to the chronological development of what has been circulated around the pandemic and the measures that have been taken according to the various languages under discussion representing several countries.
Keywords: Covid-19; Data visualization; Facebook; Multilingual; Social media analysis; Topic modeling.
© Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Figures


References
-
- Sebei H, Taieb MAH, Aouicha MB. Review of social media analytics process and big data pipeline, Social Netw Analys Mining. 2018;8:30:1–30:28.
-
- Teodorescu H-N. Using analytics and social media for monitoring and mitigation of social disasters, Procedia Engineering. 2015;107:325–334. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.06.088. - DOI
-
- Joseph JK, Dev KA, Pradeepkumar A, Mohan M (2018) Big data analytics and social media in disaster management. In: Integrating Disaster Science and Management, Elsevier, pp 287–294
-
- Landwehr PM, Carley KM (2014) Social Media in Disaster Relief, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 225–257
-
- Doan S, Vo B-KH, Collier N (2012) An analysis of twitter messages in the 2011 tohoku earthquake. In: P Kostkova, M Szomszor, D Fowler (Eds.), Electronic Healthcare, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 58–66
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
