Circulating Tumor Cells in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Mini Review
- PMID: 34764697
- PMCID: PMC8577339
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S337489
Circulating Tumor Cells in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Mini Review
Abstract
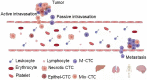
Esophageal cancer has high incidence and mortality rates and a low five-year survival rate of <15% owing to its strong capabilities of invasion, relapse and metastasis. The classic view holds that metastasis and diffusion is an advanced event during cancer progression, but recent studies show that distant diffusion of primary cancer cells may actually be an early event. Detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the circulation may indicate tumor spread, so CTCs are considered to be the key factor of metastatic cascade. In recent years, despite research progress on CTCs, there is a lack of systematic and important evidence to confirm the diagnostic, monitoring and prognostic values of CTCs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). In this review, we clarify the relationship between CTC values and ESCC and provide more reliable evidence to improve the management and treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: circulating tumor cells; diagnostic; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; prognostic.
© 2021 Shi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Ikoma D, Ichikawa D, Ueda Y, et al. Circulating tumor cells and aberrant methylation as tumor markers in patients with esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(1B):535–539. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources