Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 34764859
- PMCID: PMC8576192
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.723715
Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an intermediary state between normal aging and dementia. It has a high risk of progression in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a non-invasive brain stimulation technique used to improve cognitive deficits in patients with MCI and AD. Although previous meta-analyses included studies carried on patients with MCI and AD, few studies have analyzed patients with MCI independently. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effects and safety of rTMS on cognition function in patients with MCI and factors that may influence such effects. Methods: Data used in this study were searched and screened from different databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese Technical Periodicals (VIP), Wanfang Database, and China BioMedical Literature Database (SinoMed). The retrieved studies were carefully reviewed, data were extracted, and the quality of data was assessed. Results: A total of 12 studies involving 329 patients with MCI were included in the present meta-analysis. The analyses results revealed that rTMS improved cognitive function [standardized mean difference (SMD) = 0.83, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.44-1.22, p = 0.0009] and memory function (SMD = 0.73, 95% CI = 0.48-0.97, p < 0.00001) in the MCI + rTMS active group when compared to the sham stimulation group. The showed that: (1) cognitive improvement was more pronounced under high-frequency rTMS stimulation of multiple sites, such as the bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and (2) more than 10 rTMS stimulation sessions produced higher improvement on cognition function in patients with MCI. Conclusions: This study shows that rTMS can improve cognitive function in patients with MCI, especially when applied at high frequency, multi-site, and for a prolonged period. However, further studies are required to validate these findings and explore more effective stimulation protocols and targets. Systematic Review Registration: [http://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/], identifier: CRD 42021238708.
Keywords: cognitive function; intervention; memory; mild cognitive impairment; repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; therapy; treatment.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Lan, Chen, Ren and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
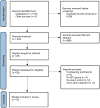
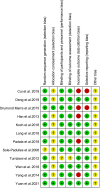
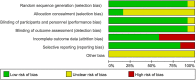







References
-
- Albert M. S., DeKosky S. T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H. H., Fox N. C., et al. . (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 270–279. 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alcalá-Lozano R., Morelos-Santana E., Cortés-Sotres J. F., Garza-Villarreal E. A., Sosa-Ortiz A. L., González-Olvera J. J. (2018). Similar clinical improvement and maintenance after rTMS at 5 Hz using a simple vs. complex protocol in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Stimul. 11, 625–627. 10.1016/j.brs.2017.12.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. Arlington: American Psychiatric Association.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

