CXCL12/SDF-1 in IgG4-Related Disease
- PMID: 34764871
- PMCID: PMC8576100
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.750216
CXCL12/SDF-1 in IgG4-Related Disease
Abstract
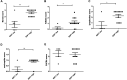
Background: SDF-1/CXCL12 is a chemokine with pleiotropic functions in hematopoietic stem cell niche homeostasis, germinal center architecture, B cell maturation, neoangiogenesis, and fibrosis. Recently, the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis was associated with cancer metastasis and autoimmune diseases. The IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a pathological condition characterized by IgG4+ plasma cells infiltrating fibrotic lesions. The aim of this research is to investigate the relevance of SDF-1/CXCL12 in IgG4-RD. Materials and Methods: Peripheral blood samples were collected before therapy from a single-center cohort of 28 IgG4-RD patients, fulfilling the ACR-EULAR classification criteria. Clinical and serological data were obtained for each patient. In total, 14 healthy donors (NHS), 9 patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), and 9 with Sjogren syndrome (SSj) were recruited as controls and screened for circulating SDF-1/CXCL12 by ELISA. Moreover, paraffin-embedded pancreatic biopsies obtained from patients with IgG4-RD (n = 7), non-autoimmune pancreatitis (n = 3), PDAC (n = 5), and control tissues (n = 4) were analyzed to study the tissue expression and localization of SDF-1/CXCL12 and one of its receptors, CXCR4, and their potential relation with neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Results: IgG4-RD patients had higher serum levels of SDF-1/CXCL12 than normal controls (p = 0.0137). Cytokine levels did not differ between the IgG4-RD autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and retroperitoneal fibrosis nor between the single- and multiple-organ involvement. No correlation was seen with the IgG4-RD Responder Index, IgG4 levels, white blood cells, or inflammatory markers in the serum. When compared to SSj, the IgG4-RD AIP subgroup presents higher amounts of serum SDF-1/CXCL12 (p = 0.0275), while no differences are seen in comparison with PDAC. The expression of SDF-1/CXCL12 in the tissue was significantly higher in the IgG4-RD tissue than the normal pancreas, and the tissue with the high SDF-1/CXCL12 expression is characterized by the overall inflammatory cell infiltration, fibrosis, and high level of NETs. Conclusion: Modulating B cell development, neoangiogenesis and fibrosis, and SDF-1/CXCL12 may play a role in IgG4-RD. The higher levels observed in IgG4-RD, as compared to SSj, which closely mimics the disease, can be related to a different pattern of lesions, with prevalent fibrosis seen in IgG4-RD. Taken together, these findings suggest that drugs acting on the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis may affect IgG4-RD.
Keywords: CXCL12; CXCR4; IgG4-related disease; NETs (neutrophil extracellular traps); fibrosis; inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Capecchi, Croia, Puxeddu, Pratesi, Cacciato, Campani, Boggi, Morelli, Tavoni and Migliorini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arai Y., Yamashita K., Kuriyama K., Shiokawa M., Kodama Y., Sakurai T., et al. (2015). Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Activation and IFN-α Production Are Prominent Features of Murine Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Human IgG4-Related Autoimmune Pancreatitis. J. Immunol. 195 (7), 3033–3044. 10.4049/jimmunol.1500971 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

