The Relationship Between Intolerance of Uncertainty and Employment Anxiety of Graduates During COVID-19: The Moderating Role of Career Planning
- PMID: 34764900
- PMCID: PMC8576396
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.694785
The Relationship Between Intolerance of Uncertainty and Employment Anxiety of Graduates During COVID-19: The Moderating Role of Career Planning
Abstract
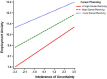
COVID-19, which is characterized by uncertainty, makes the employment anxiety of college graduates in the period of career change more and more intense. How to deal with this challenge is particularly important. The present study took career planning as a moderating variable to explore the relationship between intolerance of uncertainty (IU) and employment anxiety, as well as the role of career planning. In this quantitative study, the data of 563 college graduates from different schools were collected by using the Intolerance of Uncertainty Scale-12, Vocational Selection Anxiety Questionnaire of University Graduate, and Career Planning Scale. The final effective sample size was 550 (the overall recovery rate was 97.7%). The results of correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between IU and employment anxiety, while there was a significant negative correlation between career planning and IU, as well as the relationship between career planning and employment anxiety. The results of hierarchical regression analysis showed that IU significantly positively predicted the employment anxiety of graduates, and career planning moderated the relationship between IU and employment anxiety. These findings suggested that maintaining a sense of career planning can help college graduates get through smoothly in the face of uncertainty of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; career planning; employment anxiety; graduates; intolerance of uncertainty; purpose.
Copyright © 2021 Chen and Zeng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Individual risky and protective factors influencing university new graduates' career adaptability during COVID-19: A moderated mediation model.J Health Psychol. 2022 Sep;27(11):2632-2643. doi: 10.1177/13591053211064980. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Health Psychol. 2022. PMID: 34875928
-
Positive Information of COVID-19 and Anxiety: A Moderated Mediation Model of Risk Perception and Intolerance of Uncertainty.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 3;12:715929. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.715929. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34413803 Free PMC article.
-
Intolerance of uncertainty and anxiety among college students during the re-emergence of COVID-19: Mediation effects of cognitive emotion regulation and moderation effects of family function.J Affect Disord. 2023 Apr 14;327:378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.01.110. Epub 2023 Feb 9. J Affect Disord. 2023. PMID: 36764364 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the employment of college graduates in China and countermeasures to it.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 7;12:1390055. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1390055. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38912265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Uncertainty to Anxiety: How Uncertainty Fuels Anxiety in a Process Mediated by Intolerance of Uncertainty.Neural Plast. 2020 Nov 22;2020:8866386. doi: 10.1155/2020/8866386. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 33299402 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciding Alone or with Others: Employment Anxiety and Social Distance Predict Intuitiveness in Career Decision Making.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 13;20(2):1484. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021484. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36674244 Free PMC article.
-
Intolerance of uncertainty and future career anxiety among Chinese undergraduate students during COVID-19 period: Fear of COVID-19 and depression as mediators.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 29;10:1015446. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1015446. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36523580 Free PMC article.
-
University Experience during the First Two Waves of COVID-19: Students' Experiences and Psychological Wellbeing.Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023 Aug 11;13(8):1477-1490. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe13080108. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2023. PMID: 37623305 Free PMC article.
-
Uncertainty and Well-Being in Turkish Adults: Exploring the Role of Religiosity and Psychological Symptoms.J Relig Health. 2025 Feb 27. doi: 10.1007/s10943-025-02279-6. Online ahead of print. J Relig Health. 2025. PMID: 40016613
-
The impact of career expectation on employment anxiety of art students in higher vocational colleges during the COVID-19: A chain mediating role of social support and psychological capital.Front Psychol. 2023 Mar 14;14:1141472. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1141472. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36998359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken L. S., West S. G. (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
-
- Blustein D. L., Guarino P. A. (2020). Work and unemployment in the time of COVID-19: the existential experience of loss and fear. J. Humanist. Psychol. 60, 702–709. doi: 10.1177/0022167820934229 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources