The Utility of Exosomes in Diagnosis and Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Complications
- PMID: 34764939
- PMCID: PMC8576340
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.756581
The Utility of Exosomes in Diagnosis and Therapy of Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Complications
Abstract
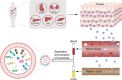
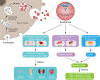
Diabetes mellitus and the associated complications are metabolic diseases with high morbidity that result in poor quality of health and life. The lack of diagnostic methods for early detection results in patients losing the best treatment opportunity. Oral hypoglycemics and exogenous insulin replenishment are currently the most common therapeutic strategies, which only yield temporary glycemic control rather than curing the disease and its complications. Exosomes are nanoparticles containing bioactive molecules reflecting individual physiological status, regulating metabolism, and repairing damaged tissues. They function as biomarkers of diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications. Considering that exosomes are bioactive molecules, can be obtained from body fluid, and have cell-type specificity, in this review, we highlight the multifold effects of exosomes in the pathology and therapy of diabetes mellitus and diabetic complications.
Keywords: biomarkers; diabetes mellitus; diagnosis; exosomes; mesenchymal stem cells; therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Tao, Wu, Zhang, Liu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures