Higher Incidence of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension After Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Asians Than in Europeans: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34765615
- PMCID: PMC8575791
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.721294
Higher Incidence of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension After Acute Pulmonary Embolism in Asians Than in Europeans: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
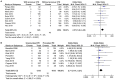
Aim: To summarize the incidence of right heart catheter diagnosed chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) after acute pulmonary embolism (PE) in a meta-analysis. Methods: Cohort studies reporting the incidence of CTEPH after acute PE were identified via search of Medline, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure and WanFang databases. Results: Twenty-two cohort studies with 5,834 acute PE patients were included. Pooled results showed that the overall incidence of CTEPH was 2.82% (95% CI: 2.11-3.53%). Subgroup analyses showed higher incidence of CTEPH in Asians than Europeans (5.08 vs. 1.96%, p = 0.01), in retrospective cohorts than prospective cohorts (4.75 vs. 2.47%, p = 0.02), and in studies with smaller sample size than those with larger sample size (4.57 vs. 1.71%, p < 0.001). Stratified analyses showed previous venous thromboembolic events and unprovoked PE were both significantly associated with increased risk of CTEPH (OR = 2.57 and 2.71, respectively; both p < 0.01). Conclusions: The incidence of CTEPH after acute PE is ~3% and the incidence is higher in Asians than Europeans. Efforts should be made for the early diagnosis and treatment of CTEPH in PE patients, particularly for high-risk population.
Keywords: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; cohort study; incidence; meta-analysis; pulmonary embolism.
Copyright © 2021 Pang, Zhang, Wang, Zhen, Zhang, Zhang, Gao, Zhang, Tao, Wan, Xie and Zhai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, Bueno H, Geersing GJ, Harjola VP, et al. . 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Respir J. (2019) 54. 10.1183/13993003.01647-2019 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

