De novo lipogenesis is elicited dramatically in human hepatocellular carcinoma especially in hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 34766116
- PMCID: PMC8491216
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.15
De novo lipogenesis is elicited dramatically in human hepatocellular carcinoma especially in hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
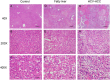
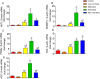
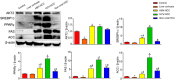
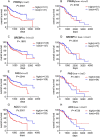
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Abnormal de novo lipogenesis is reported to be involved in hepatocarcinogenesis. In current study, de novo lipogenesis and its association with patient survival rate were investigated in human HCC samples induced by hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), or nonviral factors. Hepatic mRNA and protein levels of lipogenic transcription factors and lipid synthesis enzymes were examined by realtime-PCR (RT-PCR) and western blot. Association of gene expression and patient survival was analyzed using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data. Lipogenic pathway regulators such as AKT2, SREBP1c, PPARγ, and lipogenic enzymes such as ACC and FAS were increased in human HCC when compared with control livers. Notably, a more robust increase in de novo lipogenesis was observed in HCV-HCC when compared to HBV-HCC and nonviral HCC. High FAS and ACC expression correlated with poor overall survival (OS) in HCV-HCC. High expression of lipogenesis gene panel significantly correlated with poor OS in HCV-HCC, but not in HBV-HCC or nonviral HCC. In sum, de novo lipogenesis is stimulated dramatically in human HCC especially in HCV-HCC.
Keywords: HCV‐HCC; de novo lipogenesis; human hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2020 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- El‐Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118‐1127. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245‐1255. - PubMed
-
- Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker‐Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1625‐1638. - PubMed
-
- El‐serag HB, Tran T, Everhart JE. Diabetes increases the risk of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:460‐468. - PubMed
-
- Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010;51:1820‐1832. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
