The biological role of metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 34766124
- PMCID: PMC8491225
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.37
The biological role of metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
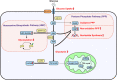
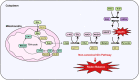
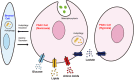
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a lethal disease and highly resistant to all forms of therapy. PDAC cells reprogram their metabolism extensively to promote their survival and growth. Reflecting the vital role of altered metabolism, experimental and clinical trials targeting the rewired metabolism are currently underway. In this review, we summarize the vital role of metabolic reprogramming in the development of PDAC and the future of novel therapeutic applications.
Keywords: autophagy; macropinocytosis; metabolism; pancreatic cancer; tumor microenvironment.
© 2020 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
