UPLC-MS/MS-based plasma lipidomics reveal a distinctive signature in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
- PMID: 34766146
- PMCID: PMC8491212
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.67
UPLC-MS/MS-based plasma lipidomics reveal a distinctive signature in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
Abstract
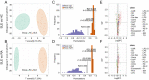
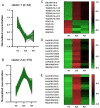
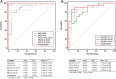
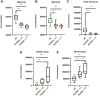
Global lipidomics is of considerable utility for exploring altered lipid profiles and unique diagnostic biomarkers in diseases. We aim to apply ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to characterize the lipidomics profile in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and explore the underlying pathogenic pathways using the lipidomics approach. Plasma samples from 18 SLE patients, 20 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and 20 healthy controls (HC) were collected. A total of 467 lipids molecular features were annotated from each sample. Orthogonal partial least square-discriminant analysis, K-mean clustering analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis indicated disrupted lipid metabolism in SLE patients, especially in phospholipid, glycerol, and sphingolipid metabolism. The area under curve (AUC) of lipid metabolism biomarkers was better than SLE inflammation markers that ordinarily used in the clinic. Proposed model of monoglyceride (MG) (16:0), MG (18:0), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) (18:3-16:0), PE (16:0-20:4), and phosphatidylcholine (PC) (O-16:2-18:3) yielded AUC 1.000 (95% CI, 1.000-1.000), specificity 100% and sensitivity 100% in the diagnosis of SLE from HC. A panel of three lipids molecular PC (18:3-18:1), PE (20:3-18:0), PE (16:0-20:4) permitted to accurately diagnosis of SLE from RA, with AUC 0.921 (95% CI, 0.828-1.000), 70% specificity, and 100% sensitivity. The plasma lipidomics signatures could serve as an efficient and accurate tool for early diagnosis and provide unprecedented insight into the pathogenesis of SLE.
Keywords: biomarkers; lipidomics; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2021 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Untargeted lipidomics reveals specific lipid abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022 May;40(5):1011-1018. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/ye2ua5. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 34251324
-
Shotgun Lipidomics Revealed Altered Profiles of Serum Lipids in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Closely Associated with Disease Activity.Biomolecules. 2018 Oct 3;8(4):105. doi: 10.3390/biom8040105. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30282943 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential lipid biomarkers for active pulmonary tuberculosis using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Feb;246(4):387-399. doi: 10.1177/1535370220968058. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33175608 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics in autoimmune diseases with main focus on systemic lupus erythematosus.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019 Sep 10;174:386-395. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019. PMID: 31207360 Review.
-
Sphingolipids and Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Organ Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:586737. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.586737. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33101319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PTEN as a prognostic factor for radiotherapy plus immunotherapy response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Apr 21;23(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03315-z. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40259377 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically predicted 486 blood metabolites concerning risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: a Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 18;13(1):22543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49233-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38110541 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Key Genes of Glutathione Metabolism in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Mendelian Randomisation, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing and Multiple Machine Learning Approaches.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70021. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70021. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40458850 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics reveals new lipid-based lung adenocarcinoma early diagnosis model.EMBO Mol Med. 2024 Apr;16(4):854-869. doi: 10.1038/s44321-024-00052-y. Epub 2024 Mar 11. EMBO Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38467839 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring genetic associations in systemic lupus erythematosus through Mendelian randomization: implications for novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):193-205. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07094-0. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39126578
References
-
- Durcan L, O'Dwyer T, Petri M. Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet. 2019;393(10188):2332–2343. - PubMed
-
- Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow M, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16039. - PubMed
-
- Fortuna G, Brennan MT. Systemic lupus erythematosus: epidemiology, pathophysiology, manifestations, and management. Dent Clin North Am. 2013;57(4):631–655. - PubMed
-
- Joo YB, Bae SC. Assessment of clinical manifestations, disease activity and organ damage in 996 Korean patientswith systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with other Asian population s. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(2):117–128. - PubMed
-
- Xiong W, Lahita R. Pragmatic approaches to therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(2):97–107. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
