Impact of rotavirus vaccine in reducing hospitalization rates in pediatric patients: a single center experience in Italy
- PMID: 34766869
- PMCID: PMC8904013
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.1978796
Impact of rotavirus vaccine in reducing hospitalization rates in pediatric patients: a single center experience in Italy
Abstract
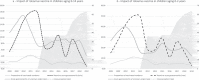
Rotavirus is a major cause of acute gastroenteritis in children under 5 years of age, with severe illness occurring in 30-40% of cases. In Italian region of Liguria, vaccination with a two-dose human attenuated vaccine was introduced in 2013. We conducted a retrospective study to assess the impact of rotavirus vaccine on hospitalizations for rotavirus-related gastroenteritis (RVGE) at the IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini. Every hospitalization due to laboratory-confirmed RVGE and acute gastroenteritis of unknown origin (AGUO) in patients aged 0-14 years in the period 2008-2019 were anonymously extracted. Vaccine coverage were obtained from the regional vaccination registry. The results were divided in 2008-2012 (before RV vaccine) and 2013-2019 (after) periods. From 2008 to 2012, there was a continuous reduction of AGUO hospitalizations while RVGE increased. Since 2013, a reduction in hospitalization rate was observed for RVGE with a sharp decrease from 17.81 per 10.000 children in 2012 to 0.79 per 10,000 in 2019, parallel with the ascending values of RV vaccination coverage that increased from 36.3% in 2013 to 63.9% in 2019. A significant negative correlation was found between the proportions of vaccinated newborns and RVGE rates (p = .012). Intussusception-related hospitalization did not show substantial modifications. We confirm vaccination as a safe practice that has a significant impact in pediatric hospitalization rates.
Keywords: Italian immunization program; Rotavirus; acute gastroenteritis; intussusception; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Linhares AC, Velázquez FR, Pérez-Schael I, Sáez-Llorens X, Abate H, Espinoza F, López P, Macías-Parra M, Ortega-Barría E, Rivera-Medina DM, et al. Efficacy and safety of an oral live attenuated human rotavirus vaccine against rotavirus gastroenteritis during the first 2 years of life in Latin American infants: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study. Lancet (London, England). 2008;371:1181–89. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60524-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical