A shared transcriptional code orchestrates temporal patterning of the central nervous system
- PMID: 34767545
- PMCID: PMC8612522
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001450
A shared transcriptional code orchestrates temporal patterning of the central nervous system
Abstract
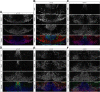
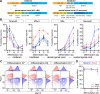
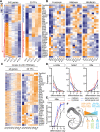
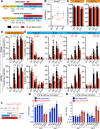
The molecular mechanisms that produce the full array of neuronal subtypes in the vertebrate nervous system are incompletely understood. Here, we provide evidence of a global temporal patterning program comprising sets of transcription factors that stratifies neurons based on the developmental time at which they are generated. This transcriptional code acts throughout the central nervous system, in parallel to spatial patterning, thereby increasing the diversity of neurons generated along the neuraxis. We further demonstrate that this temporal program operates in stem cell-derived neurons and is under the control of the TGFβ signaling pathway. Targeted perturbation of components of the temporal program, Nfia and Nfib, reveals their functional requirement for the generation of late-born neuronal subtypes. Together, our results provide evidence for the existence of a previously unappreciated global temporal transcriptional program of neuronal subtype identity and suggest that the integration of spatial and temporal patterning mechanisms diversifies and organizes neuronal subtypes in the vertebrate nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

