A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Late-Onset Pompe Disease
- PMID: 34768348
- PMCID: PMC8584814
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10214828
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Enzyme Replacement Therapy in Late-Onset Pompe Disease
Abstract
Pompe disease (PD) is a glycogen storage disorder caused by deficient activity of acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA). We sought to review the latest available evidence on the safety and efficacy of recombinant human GAA enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for late-onset PD (LOPD).
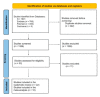
Methods: We systematically searched the MEDLINE (via PubMed), Embase, and Cochrane databases for prospective clinical studies evaluating ERT for LOPD on pre-specified outcomes. A meta-analysis was also performed.
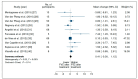
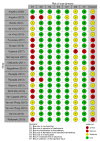
Results: Of 1601 articles identified, 22 were included. Studies were heterogeneous and with very low certainty of evidence for most outcomes. The following outcomes showed improvements associated with GAA ERT, over a mean follow-up of 32.5 months: distance walked in the 6-min walking test (6MWT) (mean change 35.7 m (95% confidence interval [CI] 7.78, 63.75)), physical domain of the SF-36 quality of life (QOL) questionnaire (mean change 1.96 (95% CI 0.33, 3.59)), and time on ventilation (TOV) (mean change -2.64 h (95% CI -5.28, 0.00)). There were no differences between the pre- and post-ERT period for functional vital capacity (FVC), Walton and Gardner-Medwin Scale score, upper-limb strength, or total SF-36 QOL score. Adverse events (AEs) after ERT were mild in most cases.
Conclusion: Considering the limitations imposed by the rarity of PD, our data suggest that GAA ERT improves 6MWT, physical QOL, and TOV in LOPD patients. ERT was safe in the studied population. PROSPERO register: 135102.
Keywords: Pompe disease; alpha-glucosidase; enzyme replacement therapy; glycogen storage disease type II.
Conflict of interest statement
P.S.K. has received research/grant support from Sanofi Genzyme, Valerion Therapeutics, Shire Pharmaceuticals, and Amicus Therapeutics. P.S.K. has received consulting fees and honoraria from Sanofi Genzyme, Shire Pharmaceuticals, Amicus Therapeutics, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Maze Therapeutics, JCR Pharmaceutical and Asklepios BioPharmaceuticalBiopharmaceutical, Inc. (AskBio). P.S.K. is a member of the Pompe and Gaucher Disease Registry Advisory Board for Sanofi Genzyme., Amicus Therapeutics, and Baebies. P.S.K. has equity in Asklepios Biopharmaceutical, Inc. (AskBio), which is developing gene therapy for Pompe disease and Maze Therapeutics, which is developing small molecule in Pompe disease. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Winchester B., Bali D., Bodamer O.A., Caillaud C., Christensen E., Cooper A., Cupler E., Deschauer M., Fumić K., Jackson M., et al. Methods for a prompt and reliable laboratory diagnosis of Pompe disease: Report from an international consensus meeting. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008;93:275–281. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.09.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

