Novel Biological and Molecular Characterization in Radiopharmaceutical Preclinical Design
- PMID: 34768368
- PMCID: PMC8584913
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10214850
Novel Biological and Molecular Characterization in Radiopharmaceutical Preclinical Design
Abstract
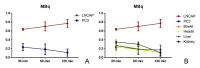
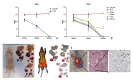
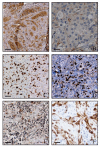
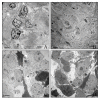
In this study, the potential of a digital autoradiography system equipped with a super resolution screen has been evaluated to investigate the biodistribution of a 18F-PSMA inhibitor in a prostate cancer mouse model. Twelve double xenograft NOD/SCID mice (LNCAP and PC3 tumours) were divided into three groups according to post-injection time points of an 18F-PSMA inhibitor. Groups of 4 mice were used to evaluate the biodistribution of the radiopharmaceutical after 30-, 60- and 120-min post-injection. Data here reported demonstrated that the digital autoradiography system is suitable to analyse the biodistribution of an 18F-PSMA inhibitor in both whole small-animal bodies and in single organs. The exposure of both whole mouse bodies and organs on the super resolution screen surface allowed the radioactivity of the PSMA inhibitor distributed in the tissues to be detected and quantified. Data obtained by using a digital autoradiography system were in line with the values detected by the activity calibrator. In addition, the image obtained from the super resolution screen allowed a perfect overlap with the tumour images achieved under the optical microscope. In conclusion, biodistribution studies performed by the autoradiography system allow the microscopical modifications induced by therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals to be studied by comparing the molecular imaging and histopathological data at the sub-cellular level.
Keywords: digital autoradiography system; nuclear imaging; pre-clinical model; radiopharmaceutical.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preclinical Investigation of Radiopharmaceuticals: An Accurate and Multidisciplinary Approach.Curr Radiopharm. 2022;15(2):157-163. doi: 10.2174/1874471014666211209154317. Curr Radiopharm. 2022. PMID: 34886790
-
More advantages in detecting bone and soft tissue metastases from prostate cancer using 18F-PSMA PET/CT.Hell J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan-Apr;22(1):6-9. doi: 10.1967/s002449910952. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hell J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30843003
-
A PSMA Ligand Labeled with Cobalt-55 for PET Imaging of Prostate Cancer.Mol Imaging Biol. 2017 Dec;19(6):915-922. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1121-7. Mol Imaging Biol. 2017. PMID: 28924629
-
Synthesis and Preclinical Characterization of the PSMA-Targeted Hybrid Tracer PSMA-I&F for Nuclear and Fluorescence Imaging of Prostate Cancer.J Nucl Med. 2019 Jan;60(1):71-78. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.212720. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30237214 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Evaluation and Pilot Clinical Study of Al18F-PSMA-BCH for Prostate Cancer PET Imaging.J Nucl Med. 2019 Sep;60(9):1284-1292. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.221671. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 30796170
Cited by
-
Impact of the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) gene testing on alcohol drinking behaviors among the Chinese Han population: study protocol of a single-center, open-label, randomized, controlled clinical trial.Trials. 2025 May 7;26(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-08851-5. Trials. 2025. PMID: 40336132 Free PMC article.
-
The ETS Homologous Factor (EHF) Represents a Useful Immunohistochemical Marker for Predicting Prostate Cancer Metastasis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;12(4):800. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040800. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453848 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

