Immunotherapy Monitoring with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Based on [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Melanomas and Lung Cancer
- PMID: 34768681
- PMCID: PMC8584484
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10215160
Immunotherapy Monitoring with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Based on [18F]FDG PET/CT in Metastatic Melanomas and Lung Cancer
Abstract
Immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors has prompted a major change not only in cancer treatment but also in medical imaging. In parallel with the implementation of new drugs modulating the immune system, new response criteria have been developed, aiming to overcome clinical drawbacks related to the new, unusual, patterns of response characterizing both solid tumors and lymphoma during the course of immunotherapy. The acknowledgement of pseudo-progression, hyper-progression, immune-dissociated response and so forth, has become mandatory for all imagers dealing with this clinical scenario. A long list of acronyms, i.e., irRC, iRECIST, irRECIST, imRECIST, PECRIT, PERCIMT, imPERCIST, iPERCIST, depicts the enormous effort made by radiology and nuclear medicine physicians in the last decade to optimize imaging parameters for better prediction of clinical benefit in immunotherapy regimens. Quite frequently, a combination of clinical-laboratory data with imaging findings has been tested, proving the ability to stratify patients into various risk groups. The next steps necessarily require a large scale validation of the most robust criteria, as well as the clinical implementation of immune-targeting tracers for immuno-PET or the exploitation of radiomics and artificial intelligence as complementary tools during the course of immunotherapy administration. For the present review article, a summary of PET/CT role for immunotherapy monitoring will be provided. By scrolling into various cancer types and applied response criteria, the reader will obtain necessary information for better understanding the potentials and limitations of the modality in the clinical setting.
Keywords: [18F]FDG PET/CT; checkpoint inhibitors; immuno-PET; immunotherapy; metabolic response; tumor response.
Conflict of interest statement
E.L. reports receiving grants from AIRC (Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro) and from the Italian Ministry of Health, and faculty remuneration from ESMIT (European School of Multimodality Imaging and Therapy) and MI&T congressi. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article exist.
Figures


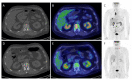
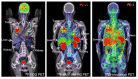
References
-
- Herbst R.S., Baas P., Kim D.W., Felip E., Pérez-Gracia J.L., Han J.Y., Molina J., Kim J.H., Arvis C.D., Ahn M.J., et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;387:1540–1550. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rittmeyer A., Barlesi F., Waterkamp D., Park K., Ciardiello F., von Pawel J., Gadgeel S.M., Hida T., Kowalski D.M., Dols M.C., et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:255–265. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

