Gastric Helicobacter suis Infection Partially Protects against Neurotoxicity in A 6-OHDA Parkinson's Disease Mouse Model
- PMID: 34768765
- PMCID: PMC8582972
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111328
Gastric Helicobacter suis Infection Partially Protects against Neurotoxicity in A 6-OHDA Parkinson's Disease Mouse Model
Abstract
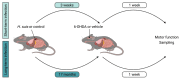
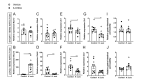
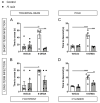
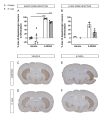
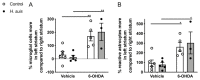
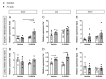
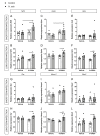
The exact etiology of Parkinson's disease (PD) remains largely unknown, but more and more research suggests the involvement of the gut microbiota. Interestingly, idiopathic PD patients were shown to have at least a 10 times higher prevalence of Helicobacter suis (H. suis) DNA in gastric biopsies compared to control patients. H. suis is a zoonotic Helicobacter species that naturally colonizes the stomach of pigs and non-human primates but can be transmitted to humans. Here, we investigated the influence of a gastric H. suis infection on PD disease progression through a 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) mouse model. Therefore, mice with either a short- or long-term H. suis infection were stereotactically injected with 6-OHDA in the left striatum and sampled one week later. Remarkably, a reduced loss of dopaminergic neurons was seen in the H. suis/6-OHDA groups compared to the control/6-OHDA groups. Correspondingly, motor function of the H. suis-infected 6-OHDA mice was superior to that in the non-infected 6-OHDA mice. Interestingly, we also observed higher expression levels of antioxidant genes in brain tissue from H. suis-infected 6-OHDA mice, as a potential explanation for the reduced 6-OHDA-induced cell loss. Our data support an unexpected neuroprotective effect of gastric H. suis on PD pathology, mediated through changes in oxidative stress.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; Helicobacter; Parkinson’s disease; gut–brain axis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Helicobacter suis causes severe gastric pathology in mouse and mongolian gerbil models of human gastric disease.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 22;5(11):e14083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014083. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124878 Free PMC article.
-
Dimethyl fumarate attenuates 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells and in animal model of Parkinson's disease by enhancing Nrf2 activity.Neuroscience. 2015 Feb 12;286:131-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.047. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 25449120
-
Naringenin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:380-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.026. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24333330
-
Helicobacter and the Potential Role in Neurological Disorders: There Is More Than Helicobacter pylori.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 28;11:584165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584165. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33633723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stomaching the Possibility of a Pathogenic Role for Helicobacter pylori in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(3):367-374. doi: 10.3233/JPD-181327. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018. PMID: 29966206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parkinson's Disease, It Takes Guts: The Correlation between Intestinal Microbiome and Cytokine Network with Neurodegeneration.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;12(1):93. doi: 10.3390/biology12010093. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastric Helicobacter species associated with dogs, cats and pigs: significance for public and animal health.Vet Res. 2022 Jun 13;53(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01059-4. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35692057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on the involvement of inflammatory mediators in Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04088-y. Online ahead of print. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40461681 Review.
-
The Spreading and Effects of Human Recombinant α-Synuclein Preformed Fibrils in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Mice.eNeuro. 2024 Mar 8;11(3):ENEURO.0024-23.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0024-23.2024. Print 2024 Mar. eNeuro. 2024. PMID: 38383588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collaborators G., Dorsey R.E., Elbaz A., Nichols E., Abd-Allah F., Abdelalim A., Adsuar J.C., Ansha M., Brayne C., Choi J.-Y.J., et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Parkinson’s Disease, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:939–953. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30295-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

