PARP-1-Associated Pathological Processes: Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols
- PMID: 34768872
- PMCID: PMC8584120
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111441
PARP-1-Associated Pathological Processes: Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols
Abstract
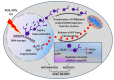
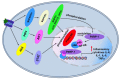
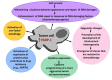
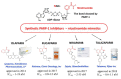
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) is a nuclear enzyme involved in processes of cell cycle regulation, DNA repair, transcription, and replication. Hyperactivity of PARP-1 induced by changes in cell homeostasis promotes development of chronic pathological processes leading to cell death during various metabolic disorders, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. In contrast, tumor growth is accompanied by a moderate activation of PARP-1 that supports survival of tumor cells due to enhancement of DNA lesion repair and resistance to therapy by DNA damaging agents. That is why PARP inhibitors (PARPi) are promising agents for the therapy of tumor and metabolic diseases. A PARPi family is rapidly growing partly due to natural polyphenols discovered among plant secondary metabolites. This review describes mechanisms of PARP-1 participation in the development of various pathologies, analyzes multiple PARP-dependent pathways of cell degeneration and death, and discusses representative plant polyphenols, which can inhibit PARP-1 directly or suppress unwanted PARP-dependent cellular processes.
Keywords: PARP-1; PARP-1 inhibitors; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and PARP Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Role in Cardiovascular Disorders.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018 Dec;18(6):493-506. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9462-2. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29968072 Review.
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 as a promising drug target for neurodegenerative diseases.Life Sci. 2021 Feb 15;267:118975. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118975. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33387580 Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP1) in Cancer: Current Developments, Therapeutic Strategies, and Future Opportunities.Med Res Rev. 2017 Nov;37(6):1461-1491. doi: 10.1002/med.21442. Epub 2017 May 16. Med Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28510338 Review.
-
Multifaceted Role of PARP-1 in DNA Repair and Inflammation: Pathological and Therapeutic Implications in Cancer and Non-Cancer Diseases.Cells. 2019 Dec 22;9(1):41. doi: 10.3390/cells9010041. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31877876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of a Mitochondria-Targeting Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 Inhibitor.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Oct 19;13(10):2868-2879. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.8b00423. Epub 2018 Sep 14. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 30184433 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IONPs-induced neurotoxicity via cascade of neuro-oxidative stress, parthanatos-mediated cell death, neuro-inflammation and neurodegenerative changes: Ameliorating effect of rosemary methanolic extract.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jan 31;14:101935. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101935. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39980662 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of DNA Repair Enzymes as a Valuable Pharmaceutical Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 27;24(9):7954. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097954. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175662 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of PARP1 Inhibitors with PARP1-Nucleosome Complexes.Cells. 2022 Oct 23;11(21):3343. doi: 10.3390/cells11213343. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359739 Free PMC article.
-
18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Alleviates P. multocida-Induced Vascular Endothelial Inflammation by PARP1-Mediated NF-κB and HMGB1 Signalling Suppression in PIEC Cells.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jun 29;16:4201-4212. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S413242. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37404255 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic and Regulatory Pathways Involved in the Anticancer Activity of Perillyl Alcohol: A Scoping Review of In Vitro Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 29;16(23):4003. doi: 10.3390/cancers16234003. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682189 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

