Biological Therapies in the Treatment of Cancer-Update and New Directions
- PMID: 34769123
- PMCID: PMC8583892
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111694
Biological Therapies in the Treatment of Cancer-Update and New Directions
Abstract
Biological therapies have changed the face of oncology by targeting cancerous cells while reducing the effect on normal tissue. This publication focuses mainly on new therapies that have contributed to the advances in treatment of certain malignancies. Immunotherapy, which has repeatedly proven to be a breakthrough therapy in melanoma, as well as B-ALL therapy with CAR T cells, are of great merit in this progress. These therapies are currently being developed by modifying bispecific antibodies and CAR T cells to improve their efficiency and bioavailability. Work on improving the therapy with oncolytic viruses is also progressing, and efforts are being made to improve the immunogenicity and stability of cancer vaccines. Combining various biological therapies, immunotherapy with oncolytic viruses or cancer vaccines is gaining importance in cancer therapy. New therapeutic targets are intensively sought among neoantigens, which are not immunocompromised, or antigens associated with tumor stroma cells. An example is fibroblast activation protein α (FAPα), the overexpression of which is observed in the case of tumor progression. Universal therapeutic targets are also sought, such as the neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase (NTRK) gene fusion, a key genetic driver present in many types of cancer. This review also raises the problem of the tumor microenvironment. Stromal cells can protect tumor cells from chemotherapy and contribute to relapse and progression. This publication also addresses the problem of cancer stem cells resistance to treatment and presents attempts to avoid this phenomenon. This review focuses on the most important strategies used to improve the selectivity of biological therapies.
Keywords: CAR T cells; biological therapy; cancer; cancer microenvironment; cancer vaccines; oncolytic viruses; recombinant antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
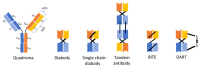
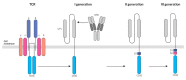
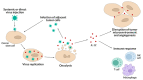
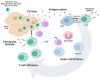
References
-
- UICC Global Cancer Control. [(accessed on 24 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.uicc.org/news/globocan-2020-new-global-cancer-data.
-
- Walewski J. Serendypity in a chase for a cure of cancer: Origin and perspectives of immunochemotherapy from nitrogen mustard to chimeric antygen receptors. Nowotwory. 2015;65:96–102. doi: 10.5603/NJO.2015.0020. - DOI
-
- Guilhot F., Schiffer C., Gambacorti-Passerini C., Niederwieser D., Resta D., Capdeville R., Zoellner U., Talpaz M., Druker B., Goldman J., et al. Hematologic and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic myelogenous leukemia. N. Eng. J. Med. 2002;346:645–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

