The Antioxidant Transcription Factor Nrf2 in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 34769371
- PMCID: PMC8585042
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111939
The Antioxidant Transcription Factor Nrf2 in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
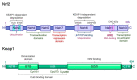
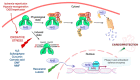
Nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor that controls cellular defense responses against toxic and oxidative stress by modulating the expression of genes involved in antioxidant response and drug detoxification. In addition to maintaining redox homeostasis, Nrf2 is also involved in various cellular processes including metabolism and inflammation. Nrf2 activity is tightly regulated at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional and post-translational levels, which allows cells to quickly respond to pathological stress. In the present review, we describe the molecular mechanisms underlying the transcriptional regulation of Nrf2. We also focus on the impact of Nrf2 in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury, a condition that stimulates the overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Finally, we analyze the protective effect of several natural and synthetic compounds that induce Nrf2 activation and protect against ischemia-reperfusion injury in the heart and other organs, and their potential clinical application.
Keywords: Nrf2 activators; cardioprotection; ischemia–reperfusion injury; ischemic conditioning; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; redox homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Moi P., Chan K., Asunis I., Cao A., Kan Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like Basic Leucine Zipper Transcriptional Activator That Binds to the Tandem NF-E2/AP1 Repeat of the Beta-Globin Locus Control Region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:9926–9930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

