Ultra-Fine Control of Silica Shell Thickness on Silver Nanoparticle-Assembled Structures
- PMID: 34769413
- PMCID: PMC8584519
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222111983
Ultra-Fine Control of Silica Shell Thickness on Silver Nanoparticle-Assembled Structures
Abstract
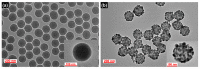
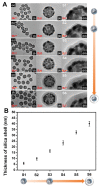
To study the distance-dependent electromagnetic field effects related to the enhancement and quenching mechanism of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) or fluorescence, it is essential to precisely control the distance from the surface of the metal nanoparticle (NP) to the target molecule by using a dielectric layer (e.g., SiO2, TiO2, and Al2O3). However, precisely controlling the thickness of this dielectric layer is challenging. Herein, we present a facile approach to control the thickness of the silica shell on silver nanoparticle-assembled silica nanocomposites, SiO2@Ag NPs, by controlling the number of reacting SiO2@Ag NPs and the silica precursor. Uniform silica shells with thicknesses in the range 5-40 nm were successfully fabricated. The proposed method for creating a homogeneous, precise, and fine silica coating on nanocomposites can potentially contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the distance-dependent electromagnetic field effects and optical properties of metal NPs.
Keywords: assembled structures; fine control; shell thickness; silica shell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kalambate P.K., Huang Z., Li Y., Shen Y., Xie M., Huang Y., Srivastava A.K. Core@ shell nanomaterials based sensing devices: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019;115:147–161. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2019.04.002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous