Angiogenesis in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disorders
- PMID: 34769465
- PMCID: PMC8584589
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222112035
Angiogenesis in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disorders
Abstract
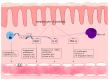
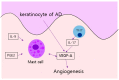
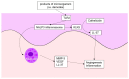
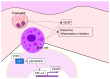
Angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels from preexisting vessels, is associated with inflammation in various pathological conditions. Well-known angiogenetic factors include vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), angiopoietins, platelet-derived growth factor, transforming growth factor-β, and basic fibroblast growth factor. Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP) and transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) have recently been added to an important angiogenic factor. Accumulating evidence indicates associations between angiogenesis and chronic inflammatory skin diseases. Angiogenesis is deeply involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. VEGF, angiopoietins, tumor necrosis factor-a, interleukin-8, and interleukin-17 are unregulated in psoriasis and induce angiogenesis. Angiogenesis may be involved in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, and in particular, mast cells are a major source of VEGF expression. Angiogenesis is an essential process in rosacea, which is induced by LL-37 from a signal cascade by microorganisms, VEGF, and MMP-3 from mast cells. In addition, angiogenesis by increased VEGF has been reported in chronic urticaria and hidradenitis suppurativa. The finding that VEGF is expressed in inflammatory skin lesions indicates that inhibition of angiogenesis is a useful strategy for treatment of chronic, inflammatory skin disorders.
Keywords: angiogenesis; atopic dermatitis; chronic urticaria; hidradenitis suppurativa; psoriasis; rosacea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara N. Angiogenesis: From Basic Science to Clinical Applications. CRC Press; New York, NY, USA: 2007. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Pathophysiology and clinical implications; pp. 1–36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

