Wood Moisture-Content Measurement Accuracy of Impregnated and Nonimpregnated Wood
- PMID: 34770343
- PMCID: PMC8588177
- DOI: 10.3390/s21217033
Wood Moisture-Content Measurement Accuracy of Impregnated and Nonimpregnated Wood
Abstract
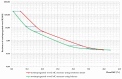
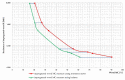
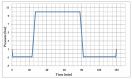
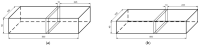
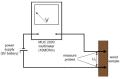
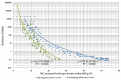
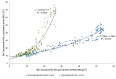
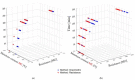
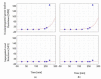
The influence of the impregnation process of pine wood (Pinus sylvestris L.) samples on the electrical resistance changes and the moisture-content measurement accuracy is presented in this paper. In this study, the resistances of impregnated and nonimpregnated green pine timber harvested from northern Poland were compared. An impregnation method based on a vacuum-pressure chamber was used. Copper salts were applied as the impregnated solutions. The obtained results of the electrical resistance comparison showed a dependence of wood resistance on the moisture content. Higher conductivity occurred in impregnated wood samples filled with copper salt compared with wood samples without impregnation. Noticeable differences in the electrical resistance values were observed when the wood moisture content was significantly above the Fibre Saturation Point (FSP).
Keywords: impregnated wood; moisture content; moisture meter resistance; pine wood; wood drying; wood moisture content; wood resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Esping B., Salin J.G., Brander P. Fukt i trä för byggindustrin. Trätek; Stockholm, Sweden: 2005. (In Swedish)
-
- Esping B. Test av kommersiella fuktkvotsmätare in-line. Trätek rapport Trätek; Stockholm, Sweden: 2003. (In Swedish)
-
- Nilsson M. Master’s thesis. Luleå University of Technology; Skellefteå, Sweden: 2010. Evaluation of Three in-Line Wood Moisture Content Meters.
-
- Vikberg T. Fuktkvotsmätare för träindustrin: En kartläggning av metoder för mätning av fuktkvoter i intervallet 7–18 fuktkvotsprocent. Technical report; Luleå University of Technology; Skellefteå, Sweden: 2010. (In Swedish)
-
- Dai G. Ahmet, K. Long-term monitoring of timber moisture content below the fiber saturation point using wood resistance sensors. For. Prod. J. 2001;51:52–58.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

