Optimized Classification of Suspended Particles in Seawater by Dense Sampling of Polarized Light Pulses
- PMID: 34770652
- PMCID: PMC8587070
- DOI: 10.3390/s21217344
Optimized Classification of Suspended Particles in Seawater by Dense Sampling of Polarized Light Pulses
Abstract
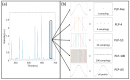
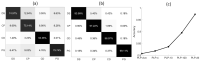
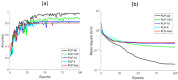
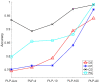
Suspended particles affect the state and vitality of the marine ecosystem. In situ probing and accurately classifying the suspended particles in seawater have an important impact on ecological research and environmental monitoring. Individual measurement of the optical polarization parameters scattered by the suspended particles has been proven to be a powerful tool to classify the particulate compositions in seawater. In previous works, the temporal polarized light pulses are sampled and averaged to evaluate the polarization parameters. In this paper, a method based on dense sampling of polarized light pulses is proposed and the experimental setup is built. The experimental results show that the dense sampling method optimizes the classification and increases the average accuracy by at least 16% than the average method. We demonstrate the feasibility of dense sampling method by classifying the multiple types of particles in mixed suspensions and show its excellent generalization ability by multi-classification of the particles. Additional analysis indicates that the dense sampling method basically takes advantage of the high-quality polarization parameters to optimize the classification performance. The above results suggest that the proposed dense sampling method has the potential to probe the suspended particles in seawater in red-tide early warning, as well as sediment and microplastics monitoring.
Keywords: classification; dense sampling; polarized light pulses; suspended particles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rao J. Coordination degree of marine biological ecological resources based on multi-source monitoring data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021;14:654. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-06993-9. - DOI
-
- Ledoux L., Turner R.K. Valuing ocean and coastal resources: A review of practical examples and issues for further action. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2002;45:583–616. doi: 10.1016/S0964-5691(02)00088-1. - DOI
-
- Mao C., Chen J., Yuan X., Yang Z., Balsam W., Ji J. Seasonal variation in the mineralogy of the suspended particulate matter of the lower Changjiang River at Nanjing, China. Clay Clay Miner. 2010;58:691–706. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2010.0580508. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

