Polish Varieties of Industrial Hemp and Their Utilisation in the Efficient Production of Lignocellulosic Ethanol
- PMID: 34770876
- PMCID: PMC8587792
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216467
Polish Varieties of Industrial Hemp and Their Utilisation in the Efficient Production of Lignocellulosic Ethanol
Abstract
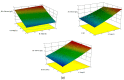
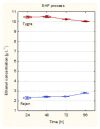
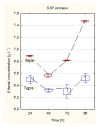
Nowadays, more and more attention is paid to the development and the intensification of the use of renewable energy sources. Hemp might be an alternative plant for bioenergy production. In this paper, four varieties of Polish industrial hemp (Białobrzeskie, Tygra, Henola, and Rajan) were investigated in order to determine which of them are the most advantageous raw materials for the effective production of bioethanol. At the beginning, physical and chemical pretreatment of hemp biomass was carried out. It was found that the most effective is the alkaline treatment with 2% NaOH, and the biomasses of the two varieties were selected for next stages of research: Tygra and Rajan. Hemp biomass before and after pretreatment was analyzed by FTIR and SEM, which confirmed the effectiveness of the pretreatment. Next, an enzymatic hydrolysis process was carried out on the previously selected parameters using the response surface methodology. Subsequently, the two approaches were analyzed: separated hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF) and a simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) process. For Tygra biomass in the SHF process, the ethanol concentration was 10.5 g∙L-1 (3.04 m3·ha-1), and for Rajan biomass at the SSF process, the ethanol concentration was 7.5 g∙L-1 (2.23 m3·ha-1). In conclusion, the biomass of Polish varieties of hemp, i.e., Tygra and Rajan, was found to be an interesting and promising raw material for bioethanol production.
Keywords: FTIR; SEM; SHF; SSF; alkaline pretreatment; bioethanol; hemp biomass; response surface methodology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and amending and subsequently repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC (Text with EEA relevance) [(accessed on 8 April 2021)]. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32009L0028.
-
- Zadrożniak B., Radwańska K., Baranowska A., Mystkowska I. Possibility of industrial hemp cultivation in areas of high nature value. Econ. Reg. Stud. 2017;10:114–127. doi: 10.2478/ers-2017-0009. - DOI
-
- Wawro A., Batog J., Gieparda W. Chemical and Enzymatic Treatment of Hemp Biomass for Bioethanol Production. Appl. Sci. 2019;9:5348. doi: 10.3390/app9245348. - DOI
-
- Bing S., Richen L., Chun Ho L., Hao W., To-Hung T., Yun Y. Recent advances and challenges of inter-disciplinary biomass valorization by integrating hydrothermal and biological techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021;135:110370.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

