Purifying and Characterizing Bacterially Expressed Soluble Lactate Dehydrogenase from Plasmodium knowlesi for the Development of Anti-Malarial Drugs
- PMID: 34771034
- PMCID: PMC8588329
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216625
Purifying and Characterizing Bacterially Expressed Soluble Lactate Dehydrogenase from Plasmodium knowlesi for the Development of Anti-Malarial Drugs
Abstract
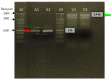
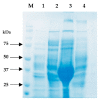
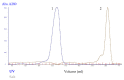
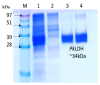
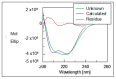
Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLH) is one of the enzymes in glycolysis with potential target for chemotherapy. This study aimed to clone, overexpress and characterize soluble recombinant lactate dehydrogenase from Plasmodium knowlesi in a bacterial system. Synthetic P. knowlesi lactate dehydrogenase (Pk-LDH) gene was cloned into pET21a expression vector, transformed into Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3) expression system and then incubated for 18 h, 20 °C with the presence of 0.5 mM isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside in Terrific broth supplemented with Magnesium sulfate, followed by protein purifications using Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography and size exclusion chromatography (SEC). Enzymatic assay was conducted to determine the activity of the enzyme. SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that protein of 34 kDa size was present in the soluble fraction. In SEC, a single peak corresponding to the size of Pk-LDH protein was observed, indicating that the protein has been successfully purified. From MALDI-TOF analysis findings, a peptide score of 282 was established, which is significant for lactate dehydrogenase from P. knowlesi revealed via MASCOT analysis. Secondary structure analysis of CD spectra indicated 79.4% α helix and 1.37% β strand structure. Specific activity of recombinant Pk-LDH was found to be 475.6 U/mg, confirming the presence of active protein. Soluble Pk-LDH that is biologically active was produced, which can be used further in other malaria studies.
Keywords: Plasmodium knowlesi; lactate dehydrogenase; malaria; protein expression; protein purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cloning, Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Lactate Dehydrogenase from Plasmodium knowlesi: A Zoonotic Malaria Parasite.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 22;25(11):5615. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115615. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891805 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, overexpression, purification and characterization of Plasmodium knowlesi lactate dehydrogenase.Protein Expr Purif. 2012 Aug;84(2):195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2012.05.008. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Protein Expr Purif. 2012. PMID: 22683723
-
Monoclonal antibodies against lactate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium knowlesi.Indian J Exp Biol. 1995 Jan;33(1):6-11. Indian J Exp Biol. 1995. PMID: 9135668
-
Inhibitors of lactate dehydrogenase isoforms and their therapeutic potentials.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(7):672-97. doi: 10.2174/092986710790416263. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20088761 Review.
-
Malaria, anti malarial drugs and the role of melatonin.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Oct;12(5):371-9. doi: 10.2174/187152612804142198. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 23082960 Review.
Cited by
-
Cloning, Expression, Purification, and Characterization of Lactate Dehydrogenase from Plasmodium knowlesi: A Zoonotic Malaria Parasite.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 22;25(11):5615. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115615. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891805 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant production, purification, and biochemical characterization of a novel L-lactate dehydrogenase from Bacillus cereus NRC1 and inhibition study of mangiferin.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 6;11:1165465. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1165465. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37091329 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary insight on diarylpentanoids as potential antimalarials: In silico, in vitro pLDH and in vivo zebrafish toxicity assessment.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 7;10(5):e27462. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27462. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38495201 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Escherichia coli Strains for Novel Production of Plasmodium ovale Lactate Dehydrogenase.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 27;12(5):876. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050876. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792706 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Malaria Report 2016. World Health Organizations; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Abeyasinghe R. Plasmodium knowlesi current status and the request for review by an Evidence Review Group Malaria Policy Advisory Committee Geneva, Switzerland; 2016. [(accessed on 2 September 2018)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/malaria/mpac/mpac-sept2016-knowlesi.pdf.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

