Volatile Compounds and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Selected Citrus Essential Oils Originated from Nepal
- PMID: 34771092
- PMCID: PMC8588556
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26216683
Volatile Compounds and Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Selected Citrus Essential Oils Originated from Nepal
Abstract
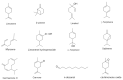
Citrus species of plants are among the most commercially cultivated crops, mainly for their fruit. Besides, the generally consumed flesh inside the fruit, the peel is quite important too. Essential oils extracted from the peel have a history of being used by humankind for centuries. These essential oils are rich in antioxidants and antimicrobial agents. Comparative investigation of volatile constituents, and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities were undertaken. The essential oils were evaluated through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and enantiomeric composition by chiral GC-MS. Similarly, the antioxidant properties were evaluated by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging assay, and antimicrobial activities were assayed using the disk diffusion method. The highest extraction yield of 1.83% was observed in Citrus sinensis Osbeck. GC-MS analysis showed limonene (63.76-89.15%), γ-terpinene (0.24-6.43%), β-pinene (0.15-6.09%), linalool (0.35-3.5%), sabinene (0.77-2.17%), myrcene (0.74-1.75%), α-terpineol (0.28-1.15%), and α-pinene (0.2-0.58%) as the major constituents of the essential oil of the Citrus species studied. For the first time, through our study, chiral terpenoids have been observed from Citrus grandis Osbeck essential oil. The order of antioxidant activity is as follows: Citrus grandis Osbeck red flesh > Citrus reticulata Blanco > Citrus sinensis Osbeck > Citrus grandis Osbeck white flesh. Except for Citrus grandis Osbeck white flesh (52.34 µL/mL), all samples demonstrated stronger antioxidant activities than those of the positive control, quercetin (5.60 µL/mL). Therefore, these essential oils can be used as a safe natural antioxidant to prevent product oxidation. Likewise, citrus peel essential oil showed antimicrobial activity against tested bacterial strains, albeit marginal.
Keywords: antibacterial activity; antioxidant; enantiomeric distribution; limonene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Li G., Xiang S., Pan Y., Long X., Cheng Y., Han L., Zhao X. Effects of Cold-Pressing and Hydrodistillation on the Active Non-Volatile Components in Lemon Essential Oil and the Effects of the Resulting Oils on Aging-Related Oxidative Stress in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2021;8:329. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.689094. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Masango P. Cleaner Production of Essential Oils by Steam Distillation. J. Clean. Prod. 2005;13:833–839. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.02.039. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous