Molecular Mechanisms of Mitotane Action in Adrenocortical Cancer Based on In Vitro Studies
- PMID: 34771418
- PMCID: PMC8582505
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13215255
Molecular Mechanisms of Mitotane Action in Adrenocortical Cancer Based on In Vitro Studies
Abstract
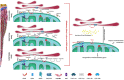
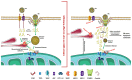
Mitotane is the only approved drug for the treatment of advanced adrenocortical carcinoma and is increasingly used for postoperative adjuvant therapy. Mitotane action involves the deregulation of cytochromes P450 enzymes, depolarization of mitochondrial membranes, and accumulation of free cholesterol, leading to cell death. Although it is known that mitotane destroys the adrenal cortex and impairs steroidogenesis, its exact mechanism of action is still unclear. The most used cell models are H295-derived cell strains and SW13 cell lines. The diverging results obtained in presumably identical cell lines highlight the need for a stable in vitro model and/or a standard methodology to perform experiments on H295 strains. The presence of several enzymatic targets responsive to mitotane in mitochondria and mitochondria-associated membranes causes progressive alteration in mitochondrial structure when cells were exposed to mitotane. Confounding factors of culture affecting in vitro experiments could reduce the significance of any molecular mechanism identified in vitro. To ensure experimental reproducibility, particular care should be taken in the choice of culture conditions: aspects such as cell strains, culture serum, lipoproteins concentration, and culture passages should be carefully considered and explicated in the presentation of results. We aimed to review in vitro studies on mitotane effects, highlighting how different experimental conditions might contribute to the controversial findings. If the concerns pointed out in this review will be overcome, the new insights into mitotane mechanism of action observed in-vitro could allow the identification of novel pharmacological molecular pathways to be used to implement personalized therapy.
Keywords: H295 strains; adrenocortical carcinoma; mitotane.
Conflict of interest statement
S.P. received a grant for scientific writing from HRA Pharma; M.T. received research grants from HRA Pharma and advisory board honoraria from HRA Pharma and Corcept Therapeutics; the other authors stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

