REV1 Inhibition Enhances Radioresistance and Autophagy
- PMID: 34771454
- PMCID: PMC8582445
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13215290
REV1 Inhibition Enhances Radioresistance and Autophagy
Abstract
Cancer therapy resistance is a persistent clinical challenge. Recently, inhibition of the mutagenic translesion synthesis (TLS) protein REV1 was shown to enhance tumor cell response to chemotherapy by triggering senescence hallmarks. These observations suggest REV1's important role in determining cancer cell response to chemotherapy. Whether REV1 inhibition would similarly sensitize cancer cells to radiation treatment is unknown. This study reports a lack of radiosensitization in response to REV1 inhibition by small molecule inhibitors in ionizing radiation-exposed cancer cells. Instead, REV1 inhibition unexpectedly triggers autophagy, which is a known biomarker of radioresistance. We report a possible role of the REV1 TLS protein in determining cancer treatment outcomes depending upon the type of DNA damage inflicted. Furthermore, we discover that REV1 inhibition directly triggers autophagy, an uncharacterized REV1 phenotype, with a significant bearing on cancer treatment regimens.
Keywords: REV1; autophagy; etoposide; ionizing radiations; radioresistance; translesion synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
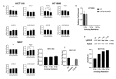
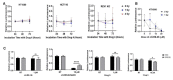
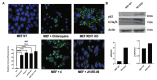
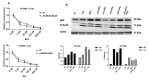
References
-
- Sail V., Rizzo A.A., Chatterjee N., Dash R.C., Ozen Z., Walker G.C., Korzhnev D.M., Hadden M.K. Identification of Small Molecule Translesion Synthesis Inhibitors That Target the Rev1-CT/RIR Protein-Protein Interaction. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017;12:1903–1912. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b01144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dash R.C., Ozen Z., McCarthy K.R., Chatterjee N., Harris C.A., Rizzo A.A., Walker G.C., Korzhnev D.M., Hadden M.K. Virtual Pharmacophore Screening Identifies Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the Rev1-CT/RIR Protein-Protein Interaction. ChemMedChem. 2019;14:1610–1617. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

