New Therapeutic Strategy for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells with Pyrazolo[3,4- d]pyrimidine Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 34771471
- PMCID: PMC8582576
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13215308
New Therapeutic Strategy for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells with Pyrazolo[3,4- d]pyrimidine Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
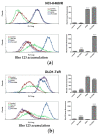
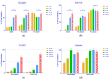
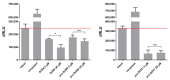
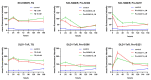
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) often interact with the multidrug resistant (MDR) phenotype of cancer cells. In some cases, TKIs increase the susceptibility of MDR cancer cells to chemotherapy. As the overexpression of membrane transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is the most common alteration in MDR cancer cells, we investigated the effects of TKI pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines on P-gp inhibition in two cellular models comprising sensitive and corresponding MDR cancer cells (human non-small cell lung carcinoma and colorectal adenocarcinoma). Tested TKIs showed collateral sensitivity by inducing stronger inhibition of MDR cancer cell line viability. Moreover, TKIs directly interacted with P-gp and inhibited its ATPase activity. Their potential P-gp binding site was proposed by molecular docking simulations. TKIs reversed resistance to doxorubicin and paclitaxel in a concentration-dependent manner. The expression studies excluded the indirect effect of TKIs on P-gp through regulation of its expression. A kinetics study showed that TKIs decreased P-gp activity and this effect was sustained for seven days in both MDR models. Therefore, pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidines with potential for reversing P-gp-mediated MDR even in prolonged treatments can be considered a new therapeutic strategy for overcoming cancer MDR.
Keywords: P-glycoprotein inhibitors; Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitors; cancer; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li W., Zhang H., Assaraf Y.G., Zhao K., Xu X., Xie J., Yang D.H., Chen Z.S. Overcoming ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance: Molecular mechanisms and novel therapeutic drug strategies. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2016;27:14–29. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2016.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

