Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients
- PMID: 34771589
- PMCID: PMC8582425
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13215426
Role of Cardiac Biomarkers in Cancer Patients
Abstract
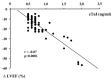
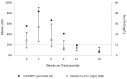
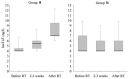
In patients with cancer-and especially some specific subtypes-the heart can be pathologically affected due to the direct action of the tumor or its secretion products or due to the toxicity of some oncological treatments. Cardiac biomarkers have been investigated as inexpensive and easily accessible tools for prediction, early diagnosis, monitoring, or prognosis of various forms of cancer-related cardiac diseases. However, their clinical usefulness was not always clearly demonstrated in every area of cardioncology. For the identification of anthracycline related cardiotoxicity in the very early stages troponins proved to be more efficient detectors than imaging methods. Nevertheless, the lack of a standardized dosage methodology and of cardiotoxicity specific thresholds, do not yet allow to outline the precise way to employ them in clinical routine and to incorporate them into appropriate diagnostic or managing algorithms. Cardiac biomarkers proved also effective in patients with primary cardiac amyloidosis, in which both troponins and natriuretic peptides were able to predict adverse outcome, and carcinoid heart disease, where a precise diagnostic cut-off for N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) was identified to screen patients with valvular involvement. Likewise, NT-proBNP proved to be an excellent predictor of postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF). On the contrary, evidence is still not sufficient to promote the routine use of cardiac biomarkers to early diagnose myocarditis due to immune check points inhibitors (ICIs), radiotherapy induced cardiotoxicity and cardiac complications related to androgenetic deprivation. In this review we present all the evidence gathered so far regarding the usefulness and limitations of these relatively inexpensive diagnostic tools in the field of cardio-oncology.
Keywords: NT-proBNP; androgen deprivation; carcinoid; cardiac amyloidosis; cardiac biomarkers; cardio-oncology; cardiotoxicity; immune check-point inhibitors; predictive; troponin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zamorano J.L., Lancellotti P., Rodriguez Muñoz D., Aboyans V., Asteggiano R., Galderisi M., Habib G., Lenihan D.J., Lip G.Y., Lyon A.R., et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: The Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017;19:9–42. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.654. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gkantaifi A., Papadopoulos C., Spyropoulou D., Toumpourleka M., Iliadis G., Kardamakis D., Nikolaou M., Tsoukalas N., Kyrgias G., Tolia M. Breast Radiotherapy and Early Adverse Cardiac Effects. The Role of Serum Biomarkers and Strain Echocardiography. Anticancer Res. 2019;39:1667–1673. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13272. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simmers D., Potgieter D., Ryan L., Fahrner R., Rodseth R.N. The Use of Preoperative B-Type Natriuretic Peptide as a Predictor of Atrial Fibrillation After Thoracic Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015;29:389–395. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2014.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

