Fracture Resistance and Failure Mode of Mandibular Molar Restored by Occlusal Veneer: Effect of Material Type and Dental Bonding Surface
- PMID: 34772003
- PMCID: PMC8585144
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14216476
Fracture Resistance and Failure Mode of Mandibular Molar Restored by Occlusal Veneer: Effect of Material Type and Dental Bonding Surface
Abstract
This study assesses the effect of the material type (lithium disilicate, zirconia, and polymer-infiltrated ceramic) and dental bonding substrates (dentin, dentin with intra-coronal cavity, and dentin with composite filling) on the fracture resistance and failure mode of molars restored by occlusal veneers.
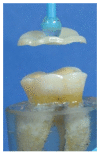
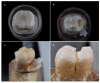
Methods: Ninety occlusal veneers, fabricated from either lithium disilicate, zirconia, or polymer-infiltrated ceramic, were adhesively bonded to teeth prepared with either dentin, dentin with intra-coronal cavity, or dentin with composite filling. All specimens were thermally aged (5000 cycles), then load cycled (120,000 cycles). Each specimen was subjected to a compressive load through fracture, then was examined (×20) to identify the fracture type. Data were statistically analyzed.
Results: Material type and dental substrate had no significant effect on the fracture resistance of adhesively retained occlusal veneer restorations. For each material, no significant differences were found between veneers bonded to dentin, dentin with intra-coronal cavity, and dentin with composite filling. Additionally, within each bonding substrate, there were no significant differences between lithium disilicate, zirconia, and polymer-infiltrated ceramic veneers. The adhesive failure was recorded mainly with zirconia occlusal veneer restorations.
Conclusions: Considering the fracture results, lithium disilicate, zirconia, and polymer-infiltrated ceramic occlusal veneers perform well whatever the type of dental bonding surface. When the dental bonding surface varies, different occlusal veneer materials should be considered. Occlusal veneers bonded to dentin, dentin with composite filling, or dentin with an intra-coronal cavity exhibited a fracture resistance exceeding the average human masticatory forces in the molar area.
Keywords: bonded restoration; non-retentive; resin cement; table-top; tooth wear.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Vailati F., Belser U.C. Full-mouth adhesive rehabilitation of a severely eroded dentition: The three-step technique. Part 1. Eur. J. Esthet. Dent. 2008;3:30–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

