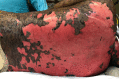
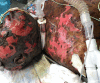
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis overlap caused by enzalutamide in patient with metastatic prostate cancer
- PMID: 34772672
- PMCID: PMC8593603
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-242319
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis overlap caused by enzalutamide in patient with metastatic prostate cancer
Keywords: dermatology; prostate cancer; skin; unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlations between clinical patterns and causes of erythema multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis: results of an international prospective study.Arch Dermatol. 2002 Aug;138(8):1019-24. doi: 10.1001/archderm.138.8.1019. Arch Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12164739
-
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An Analysis of Triggers and Implications for Improving Prevention.Am J Med. 2016 Nov;129(11):1221-1225. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.03.022. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Am J Med. 2016. PMID: 27086495
-
Comparison of reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in association with selective COX-2 inhibitors.Drug Saf. 2005;28(10):917-24. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200528100-00008. Drug Saf. 2005. PMID: 16180941
-
Current Perspectives on Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Feb;54(1):147-176. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8654-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29188475 Review.
-
[News in severe clinical adverse drug reactions: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)].Gac Med Mex. 2015 Nov-Dec;151(6):777-87. Gac Med Mex. 2015. PMID: 26581536 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Management of Skin Toxicities in Systemic Treatment of Genitourinary Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;17(2):251. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020251. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical