Drifting assemblies for persistent memory: Neuron transitions and unsupervised compensation
- PMID: 34772802
- PMCID: PMC8727022
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2023832118
Drifting assemblies for persistent memory: Neuron transitions and unsupervised compensation
Abstract
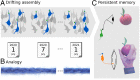
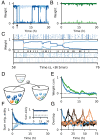
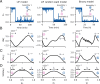
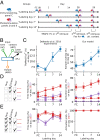
Change is ubiquitous in living beings. In particular, the connectome and neural representations can change. Nevertheless, behaviors and memories often persist over long times. In a standard model, associative memories are represented by assemblies of strongly interconnected neurons. For faithful storage these assemblies are assumed to consist of the same neurons over time. Here we propose a contrasting memory model with complete temporal remodeling of assemblies, based on experimentally observed changes of synapses and neural representations. The assemblies drift freely as noisy autonomous network activity and spontaneous synaptic turnover induce neuron exchange. The gradual exchange allows activity-dependent and homeostatic plasticity to conserve the representational structure and keep inputs, outputs, and assemblies consistent. This leads to persistent memory. Our findings explain recent experimental results on temporal evolution of fear memory representations and suggest that memory systems need to be understood in their completeness as individual parts may constantly change.
Keywords: associative memory; cell assemblies; neural representations; representational drift; synaptic remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rumpel S., Triesch J., The dynamic connectome. e-Neuroforum 22, 48–53 (2016).
-
- Humeau Y., Choquet D., The next generation of approaches to investigate the link between synaptic plasticity and learning. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1536–1543 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

