Physicians' perspectives on adverse drug reactions in pediatric routine care: a survey
- PMID: 34773600
- PMCID: PMC8761136
- DOI: 10.1007/s12519-021-00478-1
Physicians' perspectives on adverse drug reactions in pediatric routine care: a survey
Abstract
Background: Children and adolescents are at particular risk for adverse drug reactions (ADRs). We investigated physicians' perceptions on ADRs in pediatric routine care.
Methods: In this exploratory study from April to November 2020, we invited physicians treating pediatric patients across Germany to complete an online questionnaire consisting mainly of closed questions.
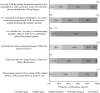
Results: Completion rate was 98% (127/129). Of all participants, 23% (29/127) stated they were not able to estimate how many of their pediatric patients experienced ADRs during drug therapy. The remaining physicians estimated that 7.5% (median; Q25/Q75 3%/20%) of their pediatric patients were affected by ADRs. Regarding counseling on ADRs, 61% (77/127) stated they do not ask regularly the extent to which parents want to be informed. In total, 26% (33/127) stated they avoid counseling on ADRs concerning commonly used approved therapies, whereas only 4% (5/127) did so concerning off-label use (P < 0.001). Altogether, 16% (20/127) stated they rather prescribe new medicines as they hope for better effectiveness; 72% (91/127) said they are cautious about doing so owing to yet unknown ADRs. Of all respondents, 46% (58/127) stated they do not report ADRs to the authorities. Concerning the black triangle symbol, a European pharmacovigilance measure, 11% (14/127) stated they knew it and 6% (7/127) stated they reported any suspected ADR for drugs with that symbol.
Conclusions: Physicians' perspectives on ADRs were ambivalent: ADRs influenced their parent counseling and drug prescribing; yet, they struggled to estimate the impact of ADRs on their patients and were not aware of specific pharmacovigilance measures.
Keywords: Adverse drug reactions; Pediatrics; Physicians; Routine care; Spontaneous reporting.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A Bertsche reports grants from UCB Pharma GmbH and honoraria for speaking engagements from Biogen GmbH, Desitin Arzneimittel GmbH, Eisai GmbH, GW Pharma GmbH, Neuraxpharm GmbH, Shire/Takeda GmbH, UCB Pharma GmbH, and ViroPharma GmbH. The other authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carnovale C, Brusadelli T, Zuccotti G, Beretta S, Sullo MG, Capuano A, et al. The importance of monitoring adverse drug reactions in pediatric patients: the results of a national surveillance program in Italy. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014;13(Suppl 1):S1–8. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2014.928692. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

